A Vlaicu II
The A Vlaicu II was the second powered airplane designed and built by Aurel Vlaicu.
| A Vlaicu II | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Monoplane |
| Manufacturer | Arts and Crafts School in Bucharest |
| Designer | Aurel Vlaicu |
| First flight | April, 1911 |
| Number built | 1 |
| Unit cost |
16,000 lei |
| Developed from | A Vlaicu I |
Design and development
The construction of A. Vlaicu Nr. II was started in December 1910 at the Școala de Arte și Meserii (Arts and Crafts School) in Bucharest, on a budget of 16,000 lei. It was an improved version of Vlaicu's earlier airplane, the A. Vlaicu Nr. I.
The A. Vlaicu Nr. II first flew in April 1911 on Cotroceni airfield in Bucharest.
Operational history
Between 23 and 30 June 1912 Vlaicu flew the A. Vlaicu Nr. II at the Die Internationale Flugwoche at Aspern near Vienna, competing against 42 other aviators including Roland Garros.[1] Vlaicu won prizes totaling 7,500 Austro-Hungarian krone for precision landing, projectile throwing and tight flying around a pole. The competition number of the A. Vlaicu Nr. II was 38, painted on the left wing and stabilizer.
On return from Aspern he performed demonstration flights throughout Transylvania at Arad, Lugoj, Hațeg, Orăștie, Vršac, Alba Iulia, Săliște, Târgu Mureș and Dumbrăveni. The year before he flew at Blaj, Sibiu, Brașov, Iași and Cernăuți.[2]
During the 1912-1913 Balkan Wars, Aurel Vlaicu flew reconnaissance missions south of Danube in the aircraft.
It was destroyed on September 13, 1913, in the crash that cost Aurel Vlaicu his life, when he attempted to make the first flight across the Carpathian Mountains. Parts from the wreckage are preserved in several Romanian museums: the Aurel Vlaicu Memorial House, the National Military Museum in Bucharest and the Aviation Museum in Bucharest.
Modern replicas

Between 2004 and 2008 a replica of the A Vlaicu II was built by Fundaţia Aerospaţială Română and Romaero in Bucharest on a budget of approximately 200,000 EUR. The airplane uses a 100 hp contemporary engine and modern materials, and has its controls modified compared to the original airplane. It was displayed at various commemorative events. In 2009 it won a bronze medal at the World Air Games (WAG) in Turin. As of 2014 the airplane has not been tested in flight.
Other scale models have been built during the last 50 years by amateurs and are on display at various Romanian museums.
Specifications (Military)
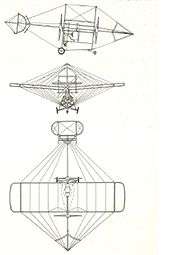
Data from [3]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 11.2 m (36 ft 9 in)
- Wingspan: 10 m (32 ft 10 in)
- Height: 4.2 m (13 ft 9 in)
- Wing area: 30 m2 (320 sq ft)
- Gross weight: 300 kg (661 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Gnome Omega air-cooled rotary piston engine, 37 kW (50 hp)
- Propellers: (2 coaxial, counter-rotating) 2-bladed Magnani/Garuda, 2.4 m (7 ft 10 in) diameter
Performance
- Maximum speed: 110 km/h (68 mph, 59 kn)
- Service ceiling: 1,000 m (3,300 ft)
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to A Vlaicu II. |
- Wiener Bilder, 30. Juni 1912
- Gheorghiu, Constantin C. (1960). Aurel Vlaicu, un precursor al aviaţiei româneşti. Bucharest: Editura Tehnică.
- Gugju, Ion; Gheorghe Iacobescu; Ovidiu Ionescu. Romanian Aeronautical Constructions 1905 - 1974. Brasov.