ARG1 (gene)
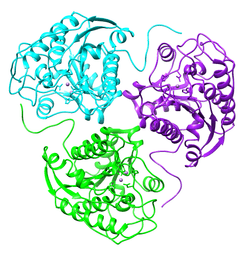
The human ARG1 gene encodes the protein arginase.[5]
Function
Arginase catalyzes the hydrolysis of arginine to ornithine and urea. At least two isoforms of mammalian arginase exist (types I and II) which differ in their tissue distribution, subcellular localization, immunologic crossreactivity and physiologic function. The type I isoform encoded by this gene, is a cytosolic enzyme and expressed predominantly in the liver as a component of the urea cycle. Inherited deficiency of this enzyme results in argininemia, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by hyperammonemia. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[6]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000118520 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000019987 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: Arginase, liver".
- [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]
External links
- Human ARG1 genome location and ARG1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Morris CR, Kato GJ, Poljakovic M, Wang X, Blackwelder WC, Sachdev V, Hazen SL, Vichinsky EP, Morris SM, Gladwin MT (July 2005). "Dysregulated arginine metabolism, hemolysis-associated pulmonary hypertension, and mortality in sickle cell disease". JAMA. 294 (1): 81–90. doi:10.1001/jama.294.1.81. PMC 2065861. PMID 15998894.
- Jiang M, Ding Y, Su Y, Hu X, Li J, Zhang Z (December 2006). "Arginase-flotillin interaction brings arginase to red blood cell membrane". FEBS Letters. 580 (28–29): 6561–4. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2006.11.003. PMID 17113085.
- Morris SM (July 2009). "Recent advances in arginine metabolism: roles and regulation of the arginases". British Journal of Pharmacology. 157 (6): 922–30. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00278.x. PMC 2737650. PMID 19508396.
- Rotondo R, Bertolotto M, Barisione G, Astigiano S, Mandruzzato S, Ottonello L, Dallegri F, Bronte V, Ferrini S, Barbieri O (May 2011). "Exocytosis of azurophil and arginase 1-containing granules by activated polymorphonuclear neutrophils is required to inhibit T lymphocyte proliferation". Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 89 (5): 721–7. doi:10.1189/jlb.1109737. PMID 21330347.
- Shapiro MB, Senapathy P (September 1987). "RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression". Nucleic Acids Research. 15 (17): 7155–74. doi:10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. PMC 306199. PMID 3658675.
- Rotondo R, Barisione G, Mastracci L, Grossi F, Orengo AM, Costa R, Truini M, Fabbi M, Ferrini S, Barbieri O (August 2009). "IL-8 induces exocytosis of arginase 1 by neutrophil polymorphonuclears in nonsmall cell lung cancer". International Journal of Cancer. 125 (4): 887–93. doi:10.1002/ijc.24448. PMID 19431148.
- Salam MT, Bastain TM, Rappaport EB, Islam T, Berhane K, Gauderman WJ, Gilliland FD (March 2011). "Genetic variations in nitric oxide synthase and arginase influence exhaled nitric oxide levels in children". Allergy. 66 (3): 412–9. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02492.x. PMC 3058253. PMID 21039601.
- Gannon PO, Godin-Ethier J, Hassler M, Delvoye N, Aversa M, Poisson AO, Péant B, Alam Fahmy M, Saad F, Lapointe R, Mes-Masson AM (August 2010). Creighton C (ed.). "Androgen-regulated expression of arginase 1, arginase 2 and interleukin-8 in human prostate cancer". PLOS ONE. 5 (8): e12107. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012107. PMC 2920336. PMID 20711410.
- Ishikawa T, Harada T, Koi H, Kubota T, Azuma H, Aso T (2007). "Identification of arginase in human placental villi". Placenta. 28 (2–3): 133–8. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2006.03.015. PMID 16720041.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.