4-Methyl-1-pentene
4-Methyl-1-pentene is used as a monomer for olefin polymerisation. The resulting polymer is poly(4-methyl-1-pentene).
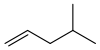 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
4-Methylpent-1-ene[1] | |
| Other names
4-Methyl-1-pentene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1731096 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.656 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3295 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12 | |
| Molar mass | 84.162 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 665 mg cm−3 |
| Melting point | −173 to −113 °C; −280 to −172 °F; 100 to 160 K |
| Boiling point | 54 °C; 129 °F; 327 K |
| Vapor pressure | 30.7 kPa (at 20 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-78.86--77.58 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
-3.99836--3.99728 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H225, H304 |
| P210, P301+310, P331 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | −7 °C (19 °F; 266 K) |
| 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- "poly(4-methyl-1-pentene) - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
