4-Mercaptophenylacetic acid
MPAA (4-Mercaptophenylacetic acid) is a redox buffer that increases the folding rate of disulfide-containing proteins.
.svg.png) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(4-sulfanylphenyl)acetic acid | |
| Preferred IUPAC name
(4-Sulfanylphenyl)acetic acid | |
| Other names
2-(4-Mercaptophenyl)acetic acid 4-Mercaptophenylacetic acid MPAA | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.156.056 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| HSC6H4CH2CO2H | |
| Molar mass | 168.21 g/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 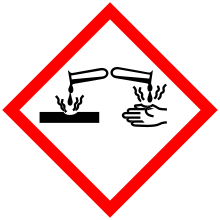  |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H315, H318, H319, H335 |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
MPAA is also used in native chemical ligation as a thiol catalyst.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.