3-Deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid
3-Deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid or keto-deoxyoctulosonate (KDO) is an ulosonic acid of a 2-ketooctose which is used by bacteria in the synthesis of lipopolysaccharides.[1] The d-manno prefix indicates that the four chiral centers have the same configuration as d-mannose.
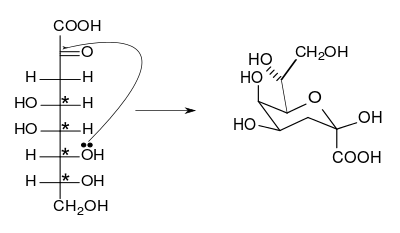
The cyclization of 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid to the β-anomer. The chiral centers are indicated by asterisks.
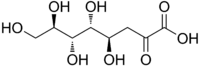 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4R,5R,6R,7R)-4,5,6,7,8-pentahydroxy-2-oxooctanoic acid | |
| Other names
2-Oxo-3-deoxy-d-mannooctonic acid 2-Keto-3-Deoxy-d-manno-octonate 2-Keto-3-deoxy-d-mannooctanoic acid 3-Deoxy-d-manno-2-octulosonic acid 3-Deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | D-KDO; KDO; dOclA |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14O8 | |
| Molar mass | 238.192 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Ghalambor, Mohammad Ali; Levine, Edward M.; Heath, Edward C. (1966). "The biosynthesis of cell wall lipopolysaccharide in Escherichia coli. III. The isolation and characterization of 3-deoxyoctulosonic acid". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 241 (13): 3207–15. PMID 4287911.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.