HSD3B2
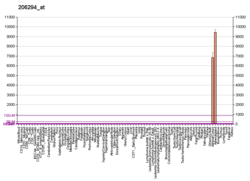
HSD3B2 is a human gene that encodes for 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta(5)-delta(4)isomerase type II or hydroxy-delta-5-steroid dehydrogenase, 3 beta- and steroid delta-isomerase 2.[5] It is expressed principally in steroidogenic tissues and is essential for steroid hormone production.[6] A notable exception is the placenta, where HSD3B1 is critical for progesterone production by this tissue.
Mutations in the HSD3B2 gene result in the condition congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000203859 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027871 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: HSD3B2 Hydroxy-delta-5-steroid dehydrogenase, 3 beta- and steroid delta-isomerase 2".
- Pelletier G, Dupont E, Simard J, Luu-The V, Bélanger A, Labrie F (October 1992). "Ontogeny and subcellular localization of 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3 beta-HSD) in the human and rat adrenal, ovary and testis". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 43 (5): 451–67. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(92)90084-V. PMID 1390295.
Further reading
- Simard J, Durocher F, Mébarki F, et al. (1996). "Molecular biology and genetics of the 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta5-delta4 isomerase gene family". J. Endocrinol. 150 Suppl: S189–207. doi:10.1677/joe.0.150S189. PMID 8943802.
- Zachmann M, Forest MG, De Peretti E (1980). "3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency. Follow-up study in a girl with pubertal bone age". Horm. Res. 11 (6): 292–302. doi:10.1159/000179067. PMID 295036.
- Rhéaume E, Simard J, Morel Y, et al. (1993). "Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to point mutations in the type II 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene". Nat. Genet. 1 (4): 239–45. doi:10.1038/ng0792-239. PMID 1363812.
- Lachance Y, Luu-The V, Verreault H, et al. (1992). "Structure of the human type II 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta 5-delta 4 isomerase (3 beta-HSD) gene: adrenal and gonadal specificity". DNA Cell Biol. 10 (10): 701–11. doi:10.1089/dna.1991.10.701. PMID 1741954.
- Rhéaume E, Lachance Y, Zhao HF, et al. (1991). "Structure and expression of a new complementary DNA encoding the almost exclusive 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta 5-delta 4-isomerase in human adrenals and gonads". Mol. Endocrinol. 5 (8): 1147–57. doi:10.1210/mend-5-8-1147. PMID 1944309.
- Morrison N, Nickson DA, McBride MW, et al. (1991). "Regional chromosomal assignment of human 3-beta-hydroxy-5-ene steroid dehydrogenase to 1p13.1 by non-isotopic in situ hybridisation". Hum. Genet. 87 (2): 223–5. doi:10.1007/BF00204189. PMID 2066113.
- Mébarki F, Sanchez R, Rhéaume E, et al. (1995). "Nonsalt-losing male pseudohermaphroditism due to the novel homozygous N100S mutation in the type II 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80 (7): 2127–34. doi:10.1210/jc.80.7.2127. PMID 7608265.
- Katsumata N, Tanae A, Yasunaga T, et al. (1995). "A novel missense mutation in the type II 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene in a family with classical salt-wasting congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency". Hum. Mol. Genet. 4 (4): 745–6. doi:10.1093/hmg/4.4.745. PMID 7633426.
- Tajima T, Fujieda K, Nakae J, et al. (1995). "Molecular analysis of type II 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene in Japanese patients with classical 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency". Hum. Mol. Genet. 4 (5): 969–71. doi:10.1093/hmg/4.5.969. PMID 7633460.
- Sanchez R, Mébarki F, Rhéaume E, et al. (1995). "Functional characterization of the novel L108W and P186L mutations detected in the type II 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene of a male pseudohermaphrodite with congenital adrenal hyperplasia". Hum. Mol. Genet. 3 (9): 1639–45. doi:10.1093/hmg/3.9.1639. PMID 7833923.
- Rhéaume E, Sanchez R, Mébarki F, et al. (1995). "Identification and characterization of the G15D mutation found in a male patient with 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3 beta-HSD) deficiency: alteration of the putative NAD-binding domain of type II 3 beta-HSD". Biochemistry. 34 (9): 2893–900. doi:10.1021/bi00009a020. PMID 7893703.
- Rhéaume E, Sanchez R, Simard J, et al. (1994). "Molecular basis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia in two siblings with classical nonsalt-losing 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 79 (4): 1012–8. doi:10.1210/jc.79.4.1012. PMID 7962268.
- Russell AJ, Wallace AM, Forest MG, et al. (1994). "Mutation in the human gene for 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II leading to male pseudohermaphroditism without salt loss". J. Mol. Endocrinol. 12 (2): 225–37. doi:10.1677/jme.0.0120225. PMID 8060486.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Sanchez R, Rhéaume E, Laflamme N, et al. (1994). "Detection and functional characterization of the novel missense mutation Y254D in type II 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3 beta HSD) gene of a female patient with nonsalt-losing 3 beta HSD deficiency". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 78 (3): 561–7. doi:10.1210/jc.78.3.561. PMID 8126127.
- Mendonça BB, Russell AJ, Vasconcelos-Leite M, et al. (1994). "Mutation in 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II associated with pseudohermaphroditism in males and premature pubarche or cryptic expression in females". J. Mol. Endocrinol. 12 (1): 119–22. doi:10.1677/jme.0.0120119. PMID 8185809.
- Chang YT, Kappy MS, Iwamoto K, et al. (1994). "Mutations in the type II 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene in a patient with classic salt-wasting 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency congenital adrenal hyperplasia". Pediatr. Res. 34 (5): 698–700. doi:10.1203/00006450-199311000-00026. PMID 8284113.
- Simard J, Rhéaume E, Sanchez R, et al. (1993). "Molecular basis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency". Mol. Endocrinol. 7 (5): 716–28. doi:10.1210/me.7.5.716. PMID 8316254.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.