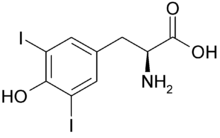
Diiodotyrosine
Diiodotyrosine (DIT) is a precursor in the production of thyroid hormone, and results from iodization of monoiodotyrosine at the other meta- position on the phenol ring.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Amino-3-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenyl)propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.539 |
| MeSH | Diiodotyrosine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H9I2NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 432.982 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Function
DIT is a modulator of the enzyme thyroid peroxidase (which is involved in the production of thyroid hormones).[1]
Triiodothyronine is formed, when diiodotyrosine is combined with monoiodotyrosine (in the colloid of the thyroid follicle).
Two molecules of DIT combine to make the thyroid hormone thyroxine ('T4' and 'T3').
gollark: Interesting. What does it do?
gollark: Or possibly `p`.
gollark: To clarify that it's a library. Of course, you would import it as potato still.
gollark: I would probably need to come up with a suitably vaguely ridiculous name, such as "libpotato".
gollark: Just use a minifier™.
See also
References
- Dème D, Fimiani E, Pommier J, Nunez J (February 1975). "Free diiodotyrosine effects on protein iodination and thyroid hormone synthesis catalyzed by thyroid peroxidase". Eur. J. Biochem. 51 (2): 329–36. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03932.x. PMID 1149735. Archived from the original on 2013-01-05.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.