Propagermanium
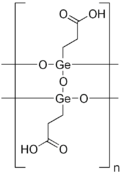
Propagermanium (INN), also known by a variety of other names including bis(2-carboxyethylgermanium) sesquioxide and 2-carboxyethylgermasesquioxane, is an organometallic compound of germanium[1] that is sold as an alternative medicine. It is a polymeric compound with the formula ((HOOCCH2CH2Ge)2O3)n.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-[(2-Carboxyethyl-oxogermyl)oxy-oxogermyl]propanoic acid | |
| Other names
proxigermanium, Ge-132, germanium sesquioxide, 2-carboxyethylgermasesquioxane, SK-818, bis(2-carboxyethylgermanium) sesquioxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.533 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O7Ge2 | |
| Molar mass | 339.4222 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The compound was first synthesized in 1967 at the Asai Germanium Research Institute in Japan. It is a water-soluble organogermanium compound used as raw material in health foods. The compound displays low toxicity in studies with rats. [2]
References
- M.P. Egorov, P.P. Gaspar (1994), Germanium: Organometallic chemistry in Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons ISBN 0-471-93620-0
- Doi, Yuko; et al. (2017). "No carcinogenicity of poly-trans-[(2-carboxyethyl) germasesquioxane] (Ge-132): 26-week feeding study using rasH2 mice". Fundamental Toxicological Sciences. 4 (3): 137–150. doi:10.2131/fts.4.137.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.