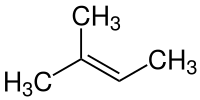
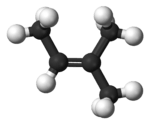
2-Methyl-2-butene
2-Methyl-2-butene, 2m2b, 2-methylbut-2-ene, also amylene is an alkene hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C5H10.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylbut-2-ene | |
| Other names
β-Isoamylene Trimethylethylene 2-Methyl-2-butene Isoamylene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.416 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2460 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10 | |
| Molar mass | 70.1329 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.662 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −134 °C (−209 °F; 139 K) |
| Boiling point | 39 °C (102 °F; 312 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility in alcohols, ether | Miscible |
| -54.14·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.385 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | < −45 °C (−49 °F; 228 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Used as a free radical scavenger in trichloromethane (chloroform) and dichloromethane (methylene chloride).
John Snow experimented with it in the 1840s as an anesthetic, but stopped using it for unknown reasons[4].
See also
References
- Dean's Handbook of Organic Chemistry, 2nd Edition.
- "Safety (MSDS) data for 2-methyl-2-butene". Archived from the original on 2009-05-14. Retrieved 2009-03-24.
- PubChem
- Caton, Donald (2000). "John Snow's practice of obstetric anesthesia". Anesthesiology: The Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists. 92 (1): 247–247.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.