2-Diphenylphosphinobenzoic acid
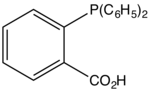
2-Diphenylphosphinobenzoic acid is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PC6H4CO2H. It is a white solid that dissolves in polar organic solvents. The ligand is a component of catalysts used for the Shell higher olefin process.[1] It is prepared by the reaction of sodium diphenylphosphide with the sodium salt of 2-chlorobenzoic acid.[2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H15O2P | |
| Molar mass | 306.301 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.278 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 174–181 °C (345–358 °F; 447–454 K) |
| alcohols, acetone, CH2Cl2 | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
GHS hazard statements |
H315, H319, H332, H335 |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Keim W; Schulz R. P. (1994). "Chelate control in the nickel-complex catalysed homogeneous oligomerization of ethylene". Journal of Molecular Catalysis. 92: 21–33. doi:10.1016/0304-5102(94)00050-6.
- Hoots, J. E.; Rauchfuss, T. B.; Wrobleski, D. A. (1982). "Substituted Triaryl Phosphines". Inorganic Syntheses. 21: 175–179. doi:10.1002/9780470132524.ch39. ISBN 9780470132524.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.