2-Butene
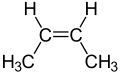
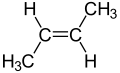
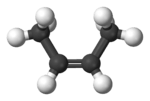
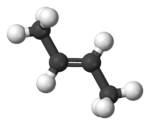
2-Butene is an acyclic alkene with four carbon atoms. It is the simplest alkene exhibiting cis/trans-isomerism (also known as (E/Z)-isomerism); that is, it exists as two geometric isomers cis-2-butene ((Z)-2-butene) and trans-2-butene ((E)-2-butene).
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
But-2-ene | |||
| Other names
β-Butylene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
| 1718755 1361341 | |||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.140 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 25196 1140 1141 | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H8 | |||
| Molar mass | 56.106 g/mol | ||
| Density | 0.641 g/mL (cis, at 3.7 °C)[1] 0.626 g/mL (trans, at 0.9 °C)[2] | ||
| Melting point | −138.9 °C (−218.0 °F; 134.2 K) (cis)[1] -105.5 °C (trans)[2] | ||
| Boiling point | 0.8 to 3.7 °C (33.4 to 38.7 °F; 273.9 to 276.8 K) (Z = 3.7 °C)[1] (E = 0.8 °C)[2] | ||
| |||
| Hazards[3] | |||
| GHS pictograms |   | ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H220 | ||
| P210, P377, P381, P403 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −72 °C (−98 °F)[1][2] | ||
| 325 °C (617 °F; 598 K)[1][2] | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related butenes |
1-Butene cis-2-Butene trans-2-Butene Isobutene | ||
Related compounds |
Butane Butyne | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
It is a petrochemical, produced by the catalytic cracking of crude oil or the dimerization of ethylene. Its main uses are in the production of gasoline (petrol) and butadiene,[4] although some 2-butene is also used to produce the solvent butanone via hydration to 2-butanol followed by oxidation.
The two isomers are extremely difficult to separate by distillation because of the proximity of their boiling points (~1 °C for cis and ~4 °C for trans[5]). However, separation is unnecessary in most industrial settings, as both isomers behave similarly in most of the desired reactions. A typical industrial 2-butene mixture is 70% (Z)-2-butene (cis-isomer) and 30% (E)-2-butene (trans-isomer). Butane and 1-butene are common impurities, present at 1% or more in industrial mixtures, which also contain smaller amounts of isobutene, butadiene and butyne.[4]
References
- Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- cis-2-Butene, International Chemical Safety Card 0397, Geneva: International Programme on Chemical Safety, March 1996. trans-2-Butene, International Chemical Safety Card 0398, Geneva: International Programme on Chemical Safety, March 1996.
- 2-Butene (PDF), SIDS Initial Assessment Report, Geneva: United Nations Environment Programme, February 1995.
- Chemical Safety Information from Intergovernmental Organizations Archived December 9, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
External links
- SIDS Initial Assessment Report for 2-Butene from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)