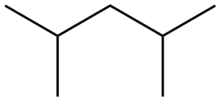
2,4-Dimethylpentane
2,4-Dimethylpentane is an alkane with the chemical formula [(H3C)2CH]2CH2. This colorless hydrocarbon is produced in large quantities in oil refineries. It results from the alkylation of isobutane by propylene.[1] Often referred to as "alkylate", it is blended with other gasoline components to give a high octane fuel. Unlike n-heptane, 2,4-dimethylpentane is a desirable fuel because its branched structure allows combustion without knocking.

Typical acid-catalyzed route to dimethylpentane.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.226 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1206 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H16 | |
| Molar mass | 100.205 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.6971 g/cm3 (0 °C) |
| Melting point | −119.9 °C (−183.8 °F; 153.2 K) |
| Boiling point | 80.4 °C (176.7 °F; 353.5 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | inflammable |
| GHS pictograms |     |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H225, H304, H315, H335, H336, H400, H410 |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P273, P280, P301+310, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P312, P321, P331, P332+313, P362, P370+378, P391, P403+233, P403+235, P405 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Bipin V. Vora; Joseph A. Kocal; Paul T. Barger; Robert J. Schmidt; James A. Johnson (2003). "Alkylation". Kirk‐Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0112112508011313.a01.pub2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.