1,4-Diazacycloheptane
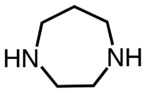
1,4-Diazacycloheptane is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)5(NH)2. This cyclic diamine is a colorless oily liquid that is soluble in polar solvents. It is studied as a chelating ligand. The N-H centers can be replaced with many other groups.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,4-Diazepane | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.288 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12N2 | |
| Molar mass | 100.165 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless oily solid |
| Melting point | 42 °C (108 °F; 315 K) |
| Boiling point | 168–170 °C (334–338 °F; 441–443 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It has known use in piperazine pharmaceuticals, for example:
Related compounds
gollark: Multiple errors on that question.
gollark: You made *multiple* errors.
gollark: I'm pretty sure I could be more right than you with my random internet knowledge and most of A-level physics.
gollark: It's not like everyone knows arbitrary electrical things. Although someone with "HV" in their name ought to.
gollark: https://tenor.com/view/lol-bees-cgp-grery-gif-14896640
References
- Musker, W. Kenneth (1992). "Coordination chemistry of bidentate medium ring ligands (mesocycles)". Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 117: 133–57. doi:10.1016/0010-8545(92)80022-J.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.