m-Phenylenediamine
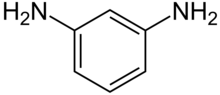
m-Phenylenediamine, also called 1,3-diaminobenzene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. It is an isomer of o-phenylenediamine and p-phenylenediamine. It is a colourless solid.
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzene-1,3-diamine | |||
| Other names
1,3-Diaminobenzene MPD | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 471357 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.259 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1673 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H8N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 108.1 | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Melting point | 64 to 66 °C (147 to 151 °F; 337 to 339 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 282 to 284 °C (540 to 543 °F; 555 to 557 K) | ||
| 42.9 g/100 ml (20 °C) | |||
| Acidity (pKa) |
| ||
| -70.53·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |     | ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H301, H311, H317, H319, H331, H341, H400, H410 | ||
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P281, P301+310, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P308+313, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P333+313, P337+313, P361, P363, P391 | |||
| Flash point | 187 °C (369 °F; 460 K) | ||
| 560 °C (1,040 °F; 833 K) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Production
m-Phenylenediamine is produced by hydrogenation of 1,3-dinitrobenzene. The dinitrobenzene is prepared by dinitration of benzene.[2]
Applications
m-Phenylenediamine is used in the preparation various polymers including aramid fibers, epoxy resins, wire enamel coatings and polyurea elastomers. Other uses for m-phenylenediamine include as an accelerator for adhesive resins, and as a component of dyes for leather and textiles. Basic Brown 1 (Bismarck Brown), Basic Orange 2, Direct Black 38, and Developed Black BH. In hair-dying, m-phenylenediamine is a "coupling agent", used to produce blue colors.[3]
References
- Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. p. 5–89. ISBN 978-1498754286.
- Smiley, Robert A. (2000), "Phenylene- and Toluenediamines", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_405, ISBN 3527306730
- Clausen, Thomas; Schwan-Jonczyk, Annette; Lang, Günther; Schuh, Werner; Liebscher, Klaus Dieter; Springob, Christian; Franzke, Michael; Balzer, Wolfgang; Imhoff, Sonja; Maresch, Gerhard; Bimczok, Rudolf (2006), "Hair Preparations", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, doi:10.1002/14356007.a12_571.pub2, ISBN 3527306730

