1,3-BAC
1,3 BAC chemically 1,3-bis(aminomethyl) cyclohexane is an organic molecule belonging to the sub class cycloaliphatic amine. It has the CAS Registry Number of 2579-20-6.[1] Its key use is as an epoxy resin curing agent.
cyclohexane.svg.png) | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.129 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H18N2 | |
| Molar mass | 142.246 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 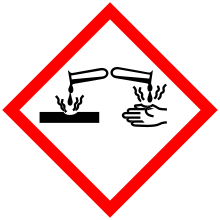  |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H302, H312, H314, H317, H318, H332, H412 |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P301+312, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P333+313, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Manufacture
It has been produced commercially as part of a mixture with the 1,4 derivative.[2] The primary route of manufacture is by catalytic hydrogenation of m-Xylylenediamine usually called MXDA.
Uses
Like most amines it maybe used as an epoxy curing agent. However, the presence of the amino group also means it can be used in polyurethane chemistry by reacting with isocyanates. In this case a polyurea would be produced. It may also be reacted with phosgene (phosgenation) to produce an isocyanate.
References
See also
German Wikipedia https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/1,3-Bis(aminomethyl)cyclohexan .