Glyceric acid
Glyceric acid is a natural three-carbon sugar acid obtained from the oxidation of glycerol.
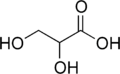 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,3-Dihydroxypropanoic acid | |
| Other names
Glyceric acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.795 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H6O4 | |
| Molar mass | 106.08 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
CH2OH-CHOH-CH2OH+[O]→CH2OH-CHOH-COOH+H2O
Biochemistry
Several phosphate derivatives of glyceric acid, including 2-phosphoglyceric acid, 3-phosphoglyceric acid, 2,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid, and 1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid, are important biochemical intermediates in glycolysis. [2]
3-phosphoglyceric acid is an important molecule for the biosynthesis of the amino acid serine, which in turn can be used in the synthesis of glycine and cysteine.
gollark: Anyway, I *do* have the GCC ARM toolchain installed.
gollark: gcc is the GTech™ C compiler, so it's good.
gollark: I assumed it was, was it not?
gollark: It *should* probably not crash the compiler horribly, to be fair.
gollark: I'm very jealous. *I* never had an ICE.
References
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 4378.
- Reece, Jane B. (2009). Biology (8th ed.). San Francisco, CA: Pearson. pp. 168–169. ISBN 978-0-8053-6844-4.
2. J.Berg,J.L.Tymoczko,L.Stryer. Biochemistry,7th edition.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.