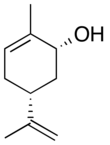
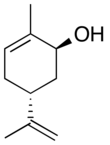
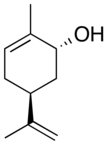
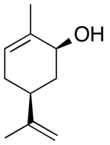
Carveol
Carveol is a natural unsaturated, monocyclic monoterpenoid alcohol that is a constituent of spearmint essential oil in the form of cis-(−)-carveol. It is a colorless fluid soluble in oils, but insoluble in water and has an odor and flavor that resemble those of spearmint and caraway. Consequently, it is used as a fragrance in cosmetics and as a flavor additive in the food industry.
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methyl-5-(prop-1-en-2-yl)cyclohex-2-en-1-ol | |||
| Other names
2-Methyl-5-(1-methylethenyl)-2-cyclohexen-1-ol Mentha-6,8-dien-2-ol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| 1861032 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.507 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Carveol | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C10H16O | |||
| Molar mass | 152.237 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 0.958 g cm−3 | ||
| Boiling point | 226 to 227 °C (439 to 441 °F; 499 to 500 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |  | ||
| GHS Signal word | Warning | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H315, H319, H335 | ||
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 98 °C (208 °F; 371 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
It has been found to exhibit chemoprevention of mammary carcinogenesis (prevents breast cancer).[1]
An alpha-trans-dihydroxy derivative, (1R,2R,6S)-3-methyl-6-(prop-1-en-2-yl)cyclohex-3-ene-1,2-diol, possesses potent antiparkinsonian activity in animal models.[2]
References
- Crowell, PL; Kennan, WS; Haag, JD; Ahmad, S; Vedejs, E; Gould, MN (1992). "Chemoprevention of mammary carcinogenesis by hydroxylated derivatives of d-limonene". Carcinogenesis. 13 (7): 1261–4. doi:10.1093/carcin/13.7.1261. PMID 1638695.
- Ardashov, Oleg V.; Pavlova, Alla V.; Il’Ina, Irina V.; Morozova, Ekaterina A.; Korchagina, Dina V.; Karpova, Elena V.; Volcho, Konstantin P.; Tolstikova, Tat’Yana G.; Salakhutdinov, Nariman F. (2011). "Highly Potent Activity of (1R,2R,6S)-3-Methyl-6-(prop-1-en-2-yl)cyclohex-3-ene-1,2-diol in Animal Models of Parkinson's Disease". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 54 (11): 3866–3874. doi:10.1021/jm2001579. PMID 21534547.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.