Fitzpatrick scale
The Fitzpatrick scale (also Fitzpatrick skin typing test; or Fitzpatrick phototyping scale) is a numerical classification schema for human skin color. It was developed in 1975 by Thomas B. Fitzpatrick as a way to estimate the response of different types of skin to ultraviolet (UV) light.[2] It was initially developed on the basis of skin color to measure the correct dose of UVA for PUVA therapy, and when the initial testing based only on hair and eye colour resulted in too high UVA doses for some, it was altered to be based on the patient's reports of how their skin responds to the sun; it was also extended to a wider range of skin types.[3][4][5] The Fitzpatrick scale remains a recognized tool for dermatological research into human skin pigmentation.
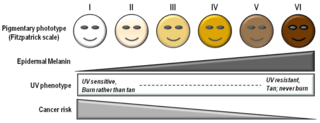
The following list shows the six categories of the Fitzpatrick scale in relation to the 36 categories of the older von Luschan scale (in parenthesis):[6][7]
- Type I (scores 0–6) always burns, never tans (palest; freckles).
- Type II (scores 7–13) usually burns, tans minimally
- Type III (scores 14–20) sometimes mild burn, tans uniformly
- Type IV (scores 21–27) burns minimally, always tans well (moderate brown)
- Type V (scores 28–34) very rarely burns, tans very easily (dark brown)
- Type VI (scores 35–36) never burns (deeply pigmented dark brown to darkest brown)
Emoji modifiers
The Fitzpatrick scale is also the basis of skin color in emoji, with 5 modifiers according to the Fitzpatrick scale (types I and II merged).
References
- D'Orazio, John; Jarrett, Stuart; Amaro-Ortiz, Alexandra; Scott, Timothy (7 June 2013). "UV Radiation and the Skin". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 14 (6): 12222–12248. doi:10.3390/ijms140612222. PMC 3709783. PMID 23749111.
- Fitzpatrick, T. B. (1975). "Soleil et peau" [Sun and skin]. Journal de Médecine Esthétique (in French) (2): 33–34
- Fitzpatrick, T.B. (1988), "The validity and practicality of sun-reactive skin types i through vi", Archives of Dermatology, 124 (6): 869–871, doi:10.1001/archderm.1988.01670060015008
- Pathak, M. A.; Jimbow, K.; Szabo, G.; Fitzpatrick, T. B. (1976). "Sunlight and melanin pigmentation". In Smith, K. C. (ed.): Photochemical and photobiological reviews, Plenum Press, New York, 1976: 211-239
- Fitzpatrick, T. B. (1986). "Ultraviolet-induced pigmentary changes: Benefits and hazards", Therapeutic Photomedicine, Karger, vol. 15 of "Current Problems in Dermatology", 1986: 25-38
- "The Fitzpatrick Skin Type Classification Scale". Skin Inc. (November 2007). Retrieved 7 January 2014.
- "Fitzpatrick Skin Type" (PDF). Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency. Retrieved 30 November 2017.