8
2
I would like to use a bash shell script from the SendTo folder. When I put a shortcut to a batch or exe into theSendTo folder it shows up in the shell Send To context submenu, but when the shortcut is pointing at a shell script it doesn't.
The OS I'm testing this on is Win7 Home Premium SP1. The extension is .sh which has been associated with MinGW's bash.exe.
My shell script has a .sh extension and I've tried disassociated the .sh extension (I think that MinGW set it up initially, but that didn't work) using this utility and tried to reassociate it to bash using:
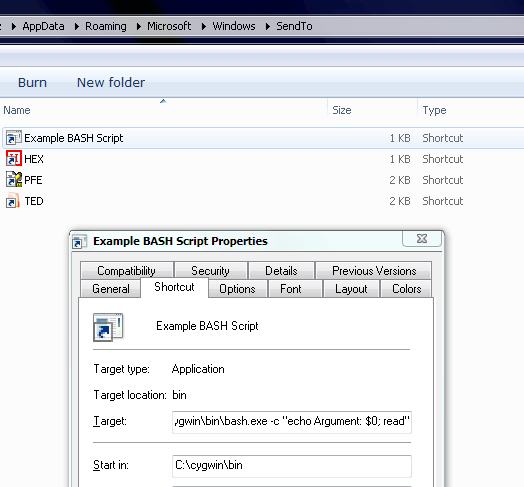
ftype ShellScript=c:\MinGW\msys\1.0\bin\bash.exe -c "'%1' %2"
assoc .sh=ShellScript
in an admin cmd shell. Though this works at a command prompt and the Explorer shell (via double click), it won't show up in the Send To menu and it won't accept a parameter by dragging a file on top of the script directly.
Does anyone know how I would do this?
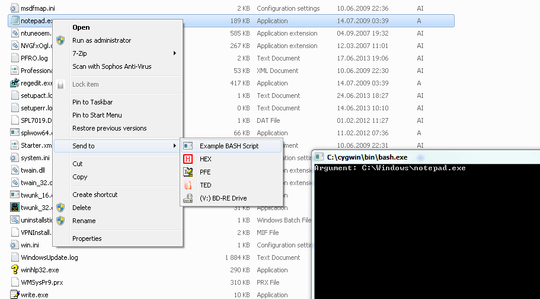
1Does Explorer run the bash shell script if you double click the shortcut to the shell script? Is the shortcut just for the shell script or for bash parameterized with the shell script? – Werner Henze – 12 years ago
what is the file extension of the script? have you established a file type association for that type? windows cannot process the bang line if it is present. which bash-for-windows are you using? – Frank Thomas – 12 years ago
@FrankThomas: I've added the additional info you requested to the question. – Adrian – 12 years ago
@WernerHenze: An attempt to drag a file over a link to the script causes a red circle with cross to appear. Attempting to put it directly over the script doesn't work either (says
Move to *dir*), so I'm thinking that it's not taking parameters for some reason even though it is executed if double clicked on. Any idea why this would be so? – Adrian – 12 years agoI don't find the answer to Werner Henze's second question, so in the similar direction: Did you try to use
c:\MinGW\msys\1.0\bin\bash.exe -c C:\Path\To\Your\Script.shas the target for the shortcut inSendTo? – mpy – 12 years ago@mpy, WernerHenze: Sorry, I think I assumed that the 2nd question had an inferred answer given
ftype ShellScript=c:\MinGW\msys\1.0\bin\bash.exe -c "'%1' %2"which shows parameters being passed. So yes, it's for a parametrised shell script. – Adrian – 12 years ago@mpy: Yes, I had tried
c:\MinGW\msys\1.0\bin\bash.exe -c C:\Path\To\Your\Script.shas the target for the shortcut inSendTois because I need to control how the parameters are laid out on the command line.-crequires a single string to be passed as the command to be invoked. Any whitespace that is not quoted results in it being considered as the next parameter for bash, not the shell script. – Adrian – 12 years ago(which BTW, seems contrary to the man page:
-c string If the -c option is present, then commands are read from string. If there are arguments after the string, they are assigned to the positional parameters, starting with $0.) – Adrian – 12 years agoThank you to @mpy for explaining what that man page quote actually means. I totally misinterpreted what it meant. – Adrian – 12 years ago