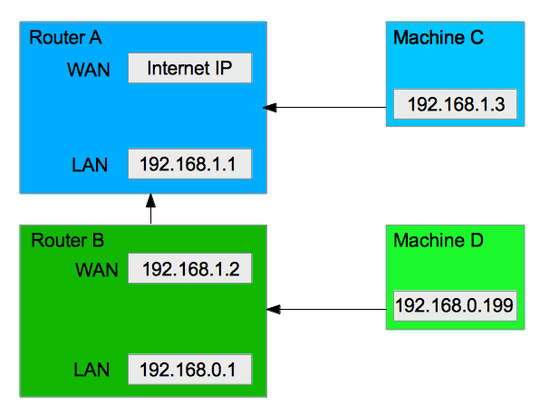
I am assuming 192.168.0.1 is not the gateway used on router B, but rather its own IP on the LAN interface. If router A is giving out addresses through DHCP, it is also informing B of what gateway to use, and this should be 192.168.1.1. If you can access the internet from B's subnet, this is the case, unless you have a very excentring setup that needs a far more detailed explanation.
To answer your question, machines C and D are on seperate networks, but D can initiate a connection with C just fine. It can't find the IP 192.168.1.3 on its own subnet, so it passes on the request to its gateway, i.e. router B, who does know where the target machine is located.
The other way around is more difficult. Neither host D itself nor its gateway, router A, knows that traffic intended for 192.168.0.199 should traverse through router B. Even if they did, for instance by defining a route '192.168.0.0/24 trough 192.168.1.2', router B would not allow the packets to pass from its WAN interface to the LAN interface.
Although you may be better off using B as a 'dumb' switch instead of a router by simply connecting everything to its LAN ports, it is possible to circumvent this issue without changing the network topology. You will need to forward ports on router B that are used in communication originating outside the 192.168.0.0/24 network.
For instance, if machine D is running a web server, to which communication must be initiated from machine C, you will want to configure router B to forward port 80 towards 192.168.0.199. Alternatively, given your router supports such a feature, you can place machine D in router B's DMZ, thus forwarding all ports to this machine, unless they are configured otherwise. Normally, this could be regarded as insecure, but in this case, the machine will still be protected through router A, unless the 192.168.1.0/24 network is compromised.
Would you clarify what you mean by communicate. Do you mean ping ftp http or access window's shares? – Keith Reynolds – 2015-08-26T22:26:23.237
Also would you indicate what kind of routers and their relative location on your network i.e. multi homed pc with linux or store bought small office / home office router like D-Link, netgear, ect. – Keith Reynolds – 2015-08-26T22:43:12.413
1Do routers A & B both hand out dhcp addresses? Also, why does B use a gateway of 192.168.0.1? – uSlackr – 2012-04-12T16:39:14.147
@uSlackr, yes both A&B hand out dhcp addresses. 192.168.0.1 is just the factory default – xiamx – 2012-04-12T16:41:30.757
I lost you here "gateway 192.168.0.1". What do you mean by gateway? Or you mean the default LAN address of router B. – None – 2012-04-12T19:41:17.833
@Radoo, 192.168.0.1 is not the gateway used on router B, but rather its own IP on the LAN interface. Sorry about that. – xiamx – 2012-04-12T19:56:06.113