1
1
I use Notepad++ and type:
read s
echo "$s"
The Output is:
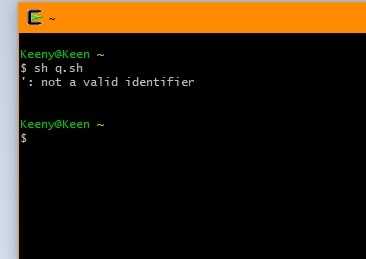
And then I try to put semicolon:
read s;
echo "$s"
and the Output is:
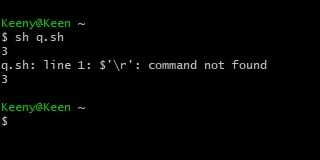
I save the file as q.sh and run with cygwin but still I cannot use read operator so I'm getting confused. I have tried other editors like vi also but the output is the same.
What is wrong? How to make it work?
3
Your file has windows-style line-endings. You need to remove them. See instructions here.
– John1024 – 2017-08-26T20:43:56.307You are also missing
#!/bin/bashas the first line of the shell script. – DavidPostill – 2017-08-26T21:13:28.990Oh Ok I got it thank you John1024 and DavidPastill – Jan Nutcha – 2017-08-27T07:52:55.443