62
15
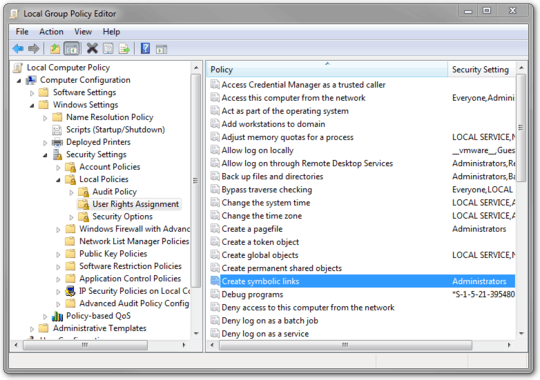
How can I grant a particular user the permission to create symlinks in Windows 7?
I've searched through "Group Policy" and Google, but haven't found anything.
On a side note, is there a way to search through everything in Group Policy Editor? The filters only seem to work on particular subtrees. I never actually found anything using the filters.
2BTW Does anybody know why creating symlinks requires admin permissions? What is so dangerous in them? – Monsignor – 2017-07-13T18:58:29.097
1@Monsignor: I saw a long time ago that Microsoft claimed too many programs couldn't handle them safely. Anyway I'm rather annoyed that they require elevation to use. – Joshua – 2017-08-24T16:25:18.787