Rufus developer here.
As correctly pointed by @magicandre1981 the version of MS-DOS provided by Rufus is the MS-DOS from Windows Millenium Edition, "uncrippled" to enable boot (I didn't invent this patch, but picked it up from the HP USB and other tools).
Also, and this is the important part, Rufus does NOT embed the MS-DOS files within the application, but picks them up from the Windows system it is running from, because, since the MS-DOS binaries are proprietary and copyrighted by Microsoft, it is illegal for anybody else but Microsoft to distribute MS-DOS binaries, be it in a zip file or an application (as a matter of fact, it appears that HP got into legal problems with Microsoft when they tried to produce a version of their HPUSBFW utility that embedded the Windows 98 MS-DOS files, and Microsoft quickly got them to stop doing that).
So, up to Windows 10, we relied on the fact that the MS-DOS files (from Windows ME) were included in the DLL (diskcopy.dll) that Windows uses to create DOS bootable floppy disks (which actually contains a complete bootable floppy FAT image), and picked the files from there, which we can legally do.
However, with the introduction of Windows 10, Microsoft dropped the ability to create bootable floppies (since nobody using Windows 10 is expected to boot from floppy) and removed diskcopy.dll. This means that we don't have a legal way to create MS-DOS bootable USB flash drives any more, and the end result is that:
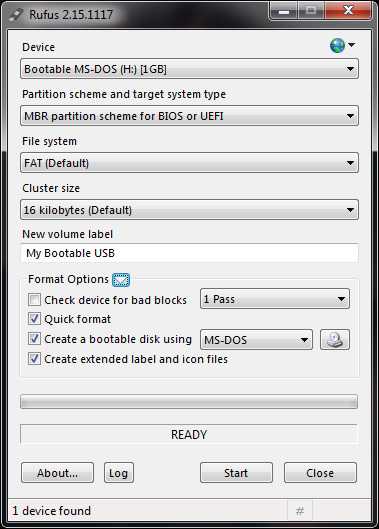
- If you use Rufus on Windows XP to Windows 8.1: you have the ability to create bootable USBs with either FreeDOS or MS-DOS (WinME edition).
- If you use Rufus on Windows 10 or later: you have the ability to create bootable USBs with FreeDOS only.
In practice, I have yet to encounter a tangible report from someone indicating that FreeDOS does not work where MS-DOS does, which is why I don't consider the loss of MS-DOS support in Windows 10 a big loss. Plus, as opposed to using MS-DOS, which is closed source and which Microsoft has stopped supporting a long time ago, FreeDOS is Open Source and actively supported, so you're usually much better off using FreeDOS.
2Out of curiosity, why do you need to know that? – Ooker – 2017-07-09T17:49:09.037
5@Ooker - A mixture of curiosity and the reasons given in my comment on the accepted answer. I mainly needed to be sure that it wasn't already DOS 6.22 and that I wasn't therefore wasting my time finding out how to create a bootable USB from 6.22. – Hashim – 2017-07-09T17:50:30.947
3Nearly every body else who does not get in license conflicts uses FreeDOS for those kind of boot disks. – eckes – 2017-07-09T19:07:05.010