Mitosis
Mitosis is the process of cell division similar to that of Meiosis but produces a clone of the original cell (known as daughter cells). The process is found in all organisms and is a way to make sure life continues.
— Outline Only —
This article is only a brief description of the subject and is not intended to give a full explanation.
Check out the "see also" or "references" sections, or Wikipedia's article for more detail.
This article is only a brief description of the subject and is not intended to give a full explanation.
Check out the "see also" or "references" sections, or Wikipedia's article for more detail.
| Live, reproduce, die Biology |
| Life as we know it |
|
| Divide and multiply |
| Greatest Great Apes |
|
v - t - e |
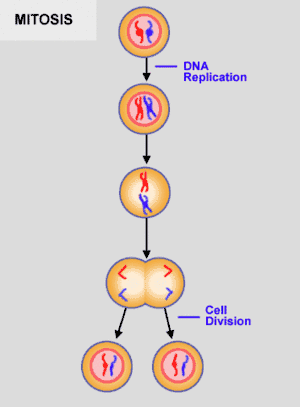
The process of Mitosis
DNA in mitosis
During mitosis, DNA will split into its two constituent strands and replicate. Two copies of the genome are then pulled to the sides of the cell while it completes the telophase and the cell undergoes cytokinesis.
gollark: Took a while to say that.
gollark: <@435756251205468160> esowiki Haskell
gollark: <@485027179286102018> ***__H A S K E L L__***
gollark: * at a low level
gollark: And without for loops.
See also
- Cell theory
This biology-related article is a stub.
You can help RationalWiki by expanding it.
You can help RationalWiki by expanding it.
This article is issued from Rationalwiki. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.