Introduction
Apple's latest creation—the iPhone 4—features a MEMS gyroscope within its pretty shell. But how does that little chip work, and what does it do?
We partnered with Chipworks to bring you an in-depth look into the science behind these micro-scale gyroscopes.
We have also completed an iPhone 4 repair manual with step-by-step repair guides to fix your own iPhone. We currently offer many iPhone 4 parts already.
-
-
Before we get into the nitty gritty of things, let's understand what a gyroscope actually does.
-
According to Wikipedia's definition, "A gyroscope is a device for measuring or maintaining orientation, based on the principles of conservation of angular momentum." The key phrase is measuring or maintaining orientation, which is the exact reason an iPhone 4 contains one of these gizmos.
-
A mechanical gyroscope - like the one shown on the left - uses a spinning rotor in the center to detect changes in orientation.
-
The iPhone 4 utilizes a microscopic, electronic version of a vibrational gyroscope, called a MEMS gyroscope.
-
-
-
A microelectromechanical system (MEMS) is an embedded system that integrates electronic and mechanical components at a very small scale.
-
A basic MEMS device consists of an ASIC and a micro-machined silicon sensor.
-
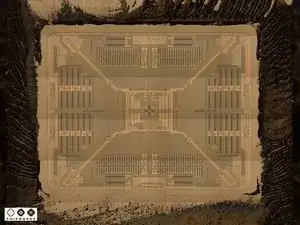
The AGD1 2022 FP6AQ chip found in the iPhone 4 is a MEMS gyroscope rumored to be designed by STMicroelectronics.
-
-
-
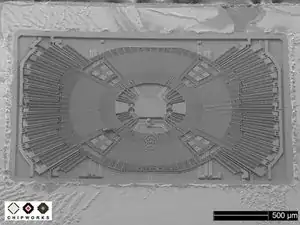
Chipworks has confirmed that the MEMS gyroscope found inside the iPhone 4 is nearly identical to an off-the-shelf STMicroelectronics L3G4200D gyroscope.
-
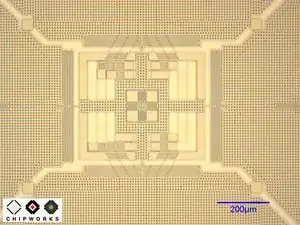
The picture of the die you see on the left is that of the GK10A MEMS die, found in the L3G4200D.
-
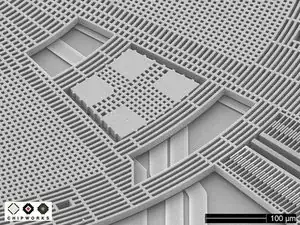
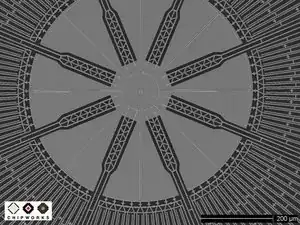
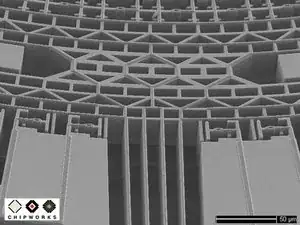
The GK10A is comprised of a plate, called the "proof mass," that vibrates (oscillates) when a drive signal is applied to set of drive capacitor plates.
-
When a user rotates the phone, the proof mass gets displaced in the X, Y, and Z directions by Coriolis forces. An ASIC processor senses the proof mass' displacement through capacitor plates located underneath the proof mass, as well as finger capacitors at the edges of the package.
-
-
-
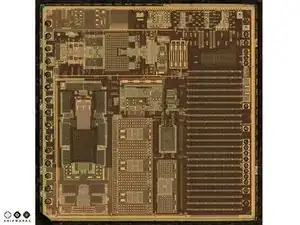
The V654A ASIC die (seen on the left) converts the tiny capacitive signals from the GK10A MEMS die into a digital signal which is fed into the iPhone 4.
-
This data is used, for example, to turn the steering wheel of a car or to aim a gun in one of iPhone 4's many video games.
-
For the mechanical engineers: the sensitivity of MEMS gyroscopes is usually in mV/dps (or degrees per second), so the output of the oscillator (in mV) divided by the sensitivity (mV/dps) provides the angular rate applied to the package, in degrees per second.
-
-
-
Shown in these photos is the ST LYPR540AH Tri-axis MEMS gyroscope, shot by a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
-
MEMS devices require extremely complicated and sensitive manufacturing procedures to produce the kind of accuracy needed for reliable sensors.
-
Most MEMS devices require a combination of deposition of a film layer, patterning to mask off areas of the deposited film to remain after etching, and etching to remove excess film to achieve the final product.
-
-
-
MEMS gyroscopes can feature awesome oscillator designs, such as this Kionix gyroscope. This kind of beauty is invisible to the naked eye, buried deep beneath a black cover.
-
The micron bars on the images give a sense of their diminutive scale. The thickness of the oscillator shown in the second picture is about a quarter the diameter of the average human hair, or about three red blood cells placed side by side.
-
-
-
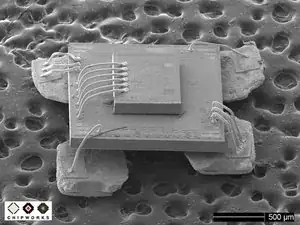
Shown here is a picture of the SiTime SI8002AC package with its outer protective casing removed.
-
An ASIC - which converts the raw signals of the oscillator - is stacked on top of the oscillator itself, and the two are wire-bonded together for signal transfer. This entire unit is completely sealed inside the plastic outer package.
-
The second picture is an X-Ray of a stacked die configuration of a Bosch BMA 220. The wire bonds connect the dies both together and to the ball grid array.
-
Stacking dies allows chip manufacturers to pack more functionality on the same footprint. This is especially important in mobile devices such as the iPhone 4, where board space is minimal.
-
-
-
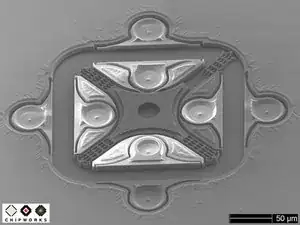
These two pictures are SEM scans of the oscillator inside the SiTime SI8002AC.
-
A great deal of engineering goes into the design, manufacture, and implementation of MEMS devices. MEMS devices truly bridge the gap between electrical and mechanical engineering, and their design involves contributions from industrial, materials, mechanical, electrical, chemical, computer, and software engineers.
-
A big thanks to Chipworks for providing the amazing images used in this teardown!
-
7 comments
That's an awesome teardown. Very cool. Another very popular gyroscope device is Wii MotionPlus by Nintendo which also contains a MEMS gyroscope, the IDG-600 manufactured by InvenSense Inc.
Thomas J -
In the 50 pic, it looks like one of the arms broke off -- wonder if you could show them the picture and get your phone replaced under warranty?
(And yes, I know those last few pictures aren't of an iPhone's gyroscope - just a joke, folks, just a joke!)
What a world we live in.
Thomas -