Please see the attached document for the service manual regarding this product.
Introduction: page 10 of PDF
Disassembling and assembling: page 31 of PDF
Service procedures: page 53 of PDF
Troubleshooting: page 59 of PDF
Preventive maintenance: page 75 of PDF
Background
Ventilators was invented in the 1940s and are commonly used in the intensive care unit at hospitals. The Maquet Servo-S is a modern ventilator used today. Ventilators are often operated by respiratory therapist, registered nurse, and critical care physicians. Ventilators are machines designed to supply oxygen in and out to the individual’s respiratory system which includes accommodating the oxygen level in a patient’s blood. For instance, the ventilator is an essential tool for helping patients during the COVID-19 pandemic as the disease created an issue affecting the functionality in the lungs.
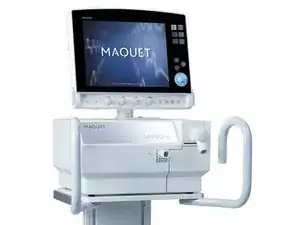
The Maquet Servo-S offers useful features such as: touch screen user interface display, inspiratory flow channel and expiratory channel. The touch screen user display supports easy navigation when operating the Maquet Servo-S. Also, the Maquet Servo-S is equipped with alarm systems and monitoring tools to provide attention to issues that may occur. The inspiratory and expiratory channels are located below the user interface display responsible for respiratory system which delivers and removes oxygen from the lungs.
Identification
The Maquet Servo-S consists of two parts: the user interface and patient unit with a control cable connecting the two parts together. The dimensions of the user interface and patient unit of the Maquet Servo- S is 380 millimeters by 300 millimeters by 520 millimeters. The user interface unit is 355 millimeters by 53 millimeters by 295 millimetres. The user interface consists of a touch screen display with functional keys on the right side, bottom and back of the user interface which allow the user to operate and manage the Maquet Servo-S.
The patient unit of the Maquet Servo-S involve two central sections of inspiratory and expiratory channels. The patient unit is 380 millimeters by 300 millimeters by 210 millimeters. The main task of the inspiratory section is to transport and provide oxygen to the patient through the inspiratory valve and pipe from the inspiratory outlet involving a 22mm / 15mm tube connector. In contrast, the expiratory section transports oxygen from the patient to the expiratory outlet with a 22mm/ 10mm tube connector.
SERVO-s Ventilator System Service Manual provided by MAQUET
Technical Specifications
General
- Power supply: 100-120V AC ± 10%, 50-60 Hz
- Battery capacity: 2 rechargeable battery modules 12 V, 5 A, 3.5 Ah each
- Dimensions (User Interface): W 355 x D 53 x H 295 mm
- Dimensions (Patient Unit): W 380 x D 300 x H 210 mm
- Dimensions (UI & PU): W 380 x D 300 x H 520 mm
- Weight: 44 pounds
- Max. airway pressure: Approximately 115 cmH2O
- Bias flow: 2 l/min
- Screen size: 31 cm (12.1”) diagonal
- Screen type: TFT-LCD module
- Screen viewing area: 246.0 x 184.5 mm
- Temperature (Operating): +50 to +104F
- Temperature (Storage): -13 to +140F
- Humidity (Operating): 15 to 95% non-condensing
- Humidity (Storage): <95% condensing
- Pressure (Operating): 660 to 1060 hPa
- Pressure (Storage): 470 to 1060 hPa
- Gas supply (Inlet gas pressure): 200–600 kPa / 2.0–6.0 bar / 29–87 PSI
- Gas delivery system (Inspiratory channel): Microprocessor controlled valve
- Pressure drop (Inspiratory channel): Max. 6 cmH2 O at a flow of 1 l/s
- Pressure drop (Expiratory channel): Max. 3 cmH2 O at a flow of 1 l/s
- Flow range (Inspiratory): 0 to 3.3 l/s
- Flow range (Expiratory): 0 to 3.2 l/s
Source: Datasheet Servo-s System version 8.0 provided by GETINGE