Background and Identification
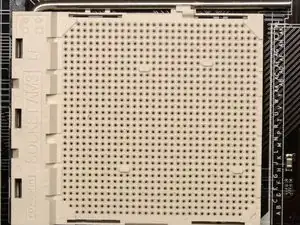
A CPU socket is a specific arrangement of electrical contacts that connect a motherboard to a processor. The AM3 socket is a specific type of CPU socket designed by AMD and released in February 2009. It is classified as a ''PGA socket'' (short for “pin grid array”) because the array of pins is located on the processor and the socket itself has holes where the pins are inserted. The AM3 socket has 941 holes, so it is also known by the name “PGA-941.”
The largest upgrade offered by the AM3 is that processors in an AM3 socket can utilize DDR3 memory. Processors in the preceding AM2 or AM2+ sockets can only use slower DDR2 memory.
AMD specifically engineering the AM3 socket to preserve some backward compatibility. Processors designed for the AM3 socket can fit in the older AM2 and AM2+ sockets and will work fine following a BIOS update (although they will only be able to use DDR2 memory). If you’re unsure of compatibility, check the manufacturer’s support page for your motherboard.
AMD released the AM3+ socket in 2011 with the addition of an extra pin. AM3 processors will work in an AM3+ socket and vice versa, as long as the motherboard can supply enough current.
The most foolproof way to determine if you have an AM3 socket is to look inside your computer. The socket is located near the center of the motherboard and will usually be somewhat covered by a CPU cooler and fan. Look under the cooler to find the socket and look for the words “socket” and an identifier like “AM3” or “AM2+.”
Technical Specifications
- Pin grid array (PGA)
- 941 pin sockets
- Supports DDR3 memory
- Can accept CPUs built for the AM3+ socket