31
5
A Faro shuffle is a technique frequently used by magicians to "shuffle" a deck. To perform a Faro shuffle you first cut the deck into 2 equal halves then you interleave the two halves. For example
[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8]
Faro shuffled is
[1 5 2 6 3 7 4 8]
This can be repeated any number of times. Interestingly enough, if you repeat this enough times, you will always end up back at the original array. For example:
[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8]
[1 5 2 6 3 7 4 8]
[1 3 5 7 2 4 6 8]
[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8]
Notice that 1 stays on the bottom and 8 stays on the top. That makes this an outer-shuffle. This is an important distinction.
The Challenge
Given an array of integers A, and a number N, output the array after N Faro shuffles. A may contain repeated or negative elements, but it will always have an even number of elements. You can assume the array will not be empty. You can also assume that N will be a non-negative integer, although it may be 0. You can take these inputs in any reasonable manner. The shortest answer in bytes wins!
Test IO:
#N, A, Output
1, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] [1, 5, 2, 6, 3, 7, 4, 8]
2, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] [1, 3, 5, 7, 2, 4, 6, 8]
7, [-23, -37, 52, 0, -6, -7, -8, 89] [-23, -6, -37, -7, 52, -8, 0, 89]
0, [4, 8, 15, 16, 23, 42] [4, 8, 15, 16, 23, 42]
11, [10, 11, 8, 15, 13, 13, 19, 3, 7, 3, 15, 19] [10, 19, 11, 3, 8, 7, 15, 3, 13, 15, 13, 19]
And, a massive test case:
23, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100]
Should output:
[1, 30, 59, 88, 18, 47, 76, 6, 35, 64, 93, 23, 52, 81, 11, 40, 69, 98, 28, 57, 86, 16, 45, 74, 4, 33, 62, 91, 21, 50, 79, 9, 38, 67, 96, 26, 55, 84, 14, 43, 72, 2, 31, 60, 89, 19, 48, 77, 7, 36, 65, 94, 24, 53, 82, 12, 41, 70, 99, 29, 58, 87, 17, 46, 75, 5, 34, 63, 92, 22, 51, 80, 10, 39, 68, 97, 27, 56, 85, 15, 44, 73, 3, 32, 61, 90, 20, 49, 78, 8, 37, 66, 95, 25, 54, 83, 13, 42, 71, 100]
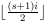
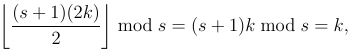
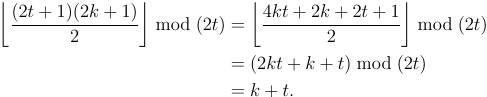
Can the array contain zero elements? – Leaky Nun – 2016-06-05T04:54:53.637
@LeakyNun We'll say no, you don't have to handle zero elements. – James – 2016-06-05T05:00:43.743
Related. Related. Related. – Martin Ender – 2016-06-05T15:12:38.327
Related – Peter Taylor – 2016-06-06T07:11:20.920
1Any permutation of a finite set, if repeated enough times, will end up back where it started; this isn't special to Faro shuffles. – Greg Martin – 2016-08-14T08:45:29.153
I guess we can assume that the elements are unique? – Titus – 2019-02-15T22:50:17.297
@titus No. A may contain negative or repeated elements. – James – 2019-02-15T22:57:14.597