63
16
A mountain is defined to be a set of line segments whose first point has coordinates (0,a) where a > 0, and whose last point has coordinates (b,0), where b > 0. All intermediate points have a y-coordinate (ordinate) strictly greater than 0. You are given the points on the mountain sorted in ascending order of x-coordinate (abscissa). Note that two points can have the same x-coordinate, producing a vertical segment of the mountain. If you are given two points with the same x-coordinate, they should be connected in the order they are given. In addition, there can be horizontal segments of the mountain These horizontal segments are not lit, no matter what. All coordinates are nonnegative integers.
The question: what is the total length of the mountain that would be lit, assuming the sun is an infinite vertical plane of light located to the right of the mountain? This number does not need to be rounded, but if it is rounded, include at least four decimal places. I have included a picture:
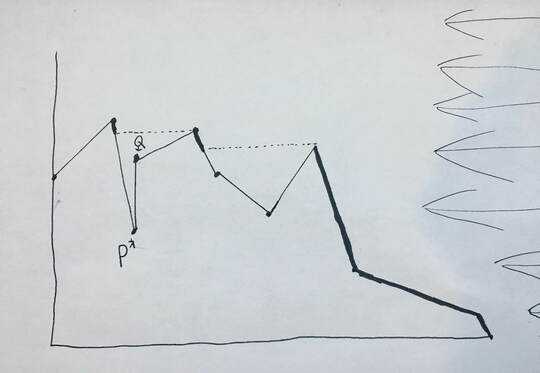 Here, the lines that are bolded represent the segments that are lit. Note that in the input, P appears before Q (PQ is a vertical line segment) so the previous point is connected to P and not Q.
Here, the lines that are bolded represent the segments that are lit. Note that in the input, P appears before Q (PQ is a vertical line segment) so the previous point is connected to P and not Q.
You may take input in any reasonable format, like a list of lists, a single list, a string, etc.
Test case:
(0,3000)
(500, 3500)
(2500, 1000)
(5000,5000)
(9000,2000)
(9000,3500)
(10200,0)
Output: 6200.0000
There are two lit-up segments here, as shown in this image: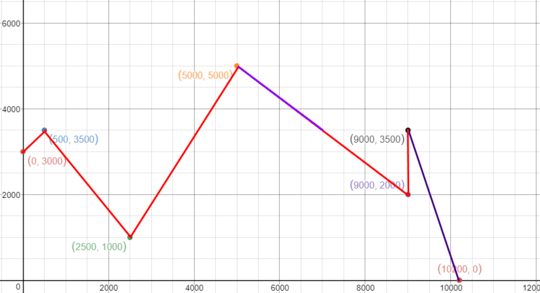 The first one has length 5000/2 = 2500 and the second one has length 3700.
The first one has length 5000/2 = 2500 and the second one has length 3700.
This is code-golf, so the shortest answer in bytes wins.
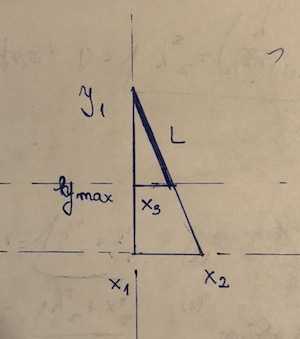
1Hint: When finding the length of a segment, there are three points you need to consider: the two endpoints, and the point that is "blocking" it (in the 2nd picture, that would be (9000,3500) which determines the length of the 3-4-5 segment. Let the two points on the main segment be
(x1, y1)and(x2,y2). The point which is "blocking" it is(x3, y3). Assume y2 < y3 <= y1. Then the length of the segment is((y1 - y3)/(y1 - y2))*sqrt((x1 - x2)^2 + (y1 - y2)^2). This is essentially the distance formula, multiplied by the fraction of the segment which is actually used. – rigged – 2017-12-22T00:33:53.8101May the mountain be horizontal? – user202729 – 2017-12-22T01:54:37.857
Yes, there can be horizontal segments on the mountain. However it will go to 0 at some point. – rigged – 2017-12-22T01:55:55.780
1But should they be lit? – user202729 – 2017-12-22T02:01:58.983
They are not lit. The light, being perfectly horizontal, can only run parallel to them and never strike them. I edited the problem to clarify this. – rigged – 2017-12-22T02:05:23.650
May we take input as two lists, one with x coordinates and one with y coordinates? – Mr. Xcoder – 2017-12-22T08:38:11.770
Test case:
(0, 100) (10, 25) (20, 50) (30, 25) (40, 75) (50, 0)(shadow cast by a peak that's not a direct neighbour). – Quentin – 2017-12-22T12:46:20.747Yes, a shadow can be cast by a peak that is not a neighbor. I guess I can add another test case to cover that. – rigged – 2017-12-22T13:21:44.160
@mrxcoder I would classify that as a reasonable input format, yes. – rigged – 2017-12-22T13:23:08.567
@imallett All I’m saying is, a problem “find the total length of the mountain” wouldn’t bee all that interesting. – rigged – 2017-12-22T13:27:20.177
Some notes:
1. Generally we leave challenges in the sandbox for at least 24 hours, because not everyone is in the same timezone as you are. 2 hours is too short in my opinion.2Also, you should shorten the sandbox post, because it's still visible to moderators and users with ≥ 2000 reputation.3[tag:code-golf]need a pair of square brackets: [tag:code-golf]. – user202729 – 2017-12-22T14:38:33.233Yeah I will collapse the sandbox post edit: i see you did it, thanks – rigged – 2017-12-22T14:39:47.423
Good idea about scanning in a hand-drawn picture for a challenge. – Magic Octopus Urn – 2018-01-19T19:33:38.313