17
2
The main purpose of the RGB (Red Green Blue) color model is for the sensing, representation and display of images in electronic systems, such as televisions and computers
HSL (Hue Saturation Lightness) is an alternative color model, designed in the 1970s by computer graphics researchers to more closely align with the way human vision perceives color-making attributes
Here are the wiki articles for RGB and HSL. It is common for graphics programs to do the calculations in HSL, and later convert to the preferred format for most screens: RGB.
The task is to write a function/program that takes HSL as an input and outputs RGB.
You can pick your preferred representation for I/O, as long as its consistent between them.
For example, they can be an array/tuple with 3 elements or an object with 3 properties named h, s, and l, but I'll accept other clever variations, like receiving the hsl as an integer (losing precision) and outputting an rgb integer.
The input can be assumed to be safe in range and format, both of which you can decide. I strongly suggest either the ranges 0-1 0-1 0-1 or 0-360 0-100 0-100 for hsl, and 0-1 0-1 0-1 or 0-255 0-255 0-255 for rgb.
Each answer is required to specify both of the above, and do put various variations in your answers if you're particularly proud of them, even if they don't have less characters than your other variations. Put the smallest on top.
Pseudo test cases for 0-360 0-100 0-100 → 0-255 0-255 0-255
h s l → r g b
0 0 0 → 0 0 0
90 56 17 → 43 68 19
202 19 39 → 81 104 118
72 55 26 → 88 103 30
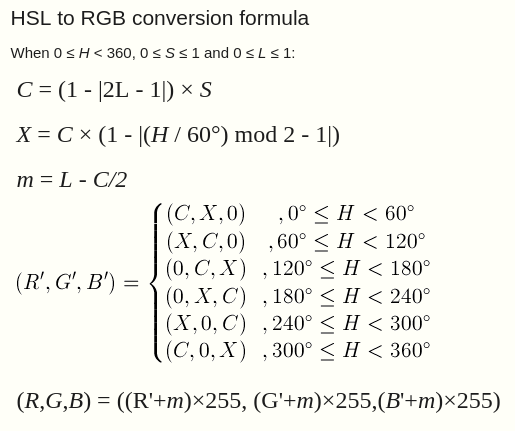
The formulae for the conversion can be found here:

This as a nice way to visualize the conversion:

Your suggested range for
Hof0-360is[0,360), would it be better written as0-359? – Jonathan Allan – 2017-12-09T21:02:48.3173@JonathanAllan I think it might look slightly more confusing, as to me, that suggests that 395.1 is not a possible input. If anything, using the
a-bnotation is wrong in itself when dealing with non-integer values, but I'd say it's ok to keep the question more readable. If anyone else complains, I'll rethink it, so thanks for pointing that out – towc – 2017-12-09T21:35:11.747Yeah, agreed on the 359.1 point - maybe just use the standard notation of
[0,360)then :) – Jonathan Allan – 2017-12-09T21:47:15.107surprised to see no glsl answers ;) – towc – 2017-12-10T19:03:37.293