4
1
The challenge is to take any real number as input and output or return the absolute value. You may not use any built-in functions other than those dealing with input and output/returning. This is code golf, so the shortest code wins. This is my first question here, so bear with me if I've left something obvious out of the challenge.
As per Quincunx's suggestion, I am limiting input to anywhere between -9E99 and 9E99.
Also, the only functions/operators you can use are input, output, return, +, -, *, /, %, ^ +=, -=, *=, /=, >, <, ==, >=, <=, !=, square, and square root or their equivalents
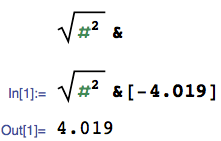
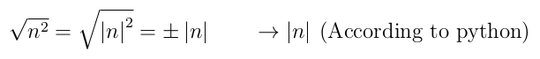
What if absolute is a single-characters math operator in my language? – Adám – 2015-12-02T11:02:31.510
Sorry @NBZ but it's not one of the acceptable functions/operators in the last lines. – Timtech – 2015-12-04T12:04:02.750
4Apart from the fact that the question as currently written seems to permit a whitelist of operators but only if they're not built in to the language, this is a classic example of why trying to whitelist permitted operations is a disaster. Consider
>: in some languages it returns0or1; in other languages it returnstrueorfalseand Booleans can't be cast to integers. Should languages in the second category be permitted to use?:in contexts which could be algebraically rewritten in terms of the condition as0or1under the "or their equivalents" grant? It's extremely fuzzy – Peter Taylor – 2015-12-14T11:34:57.833Does putting the value on the stack count as returning it? – cat – 2015-12-14T11:53:26.470
Is the program allowed to loop forever and continue receiving input, finding the absolute value, and outputting it? – Justin – 2013-12-07T00:59:24.340
take any real number as input. I believe that no program can do this. Most solutions here won't work for
-10^-googolfor instance. Maybe you should restrict it to double values or something similar. But the what about -π? Programs that only allow doubles wouldn't work. Also, what about something like π-4? – Justin – 2013-12-07T05:47:46.437My answers can handle all these values @Quincunx – Timtech – 2013-12-07T11:11:54.600
And yes, it is allowed to loop if you want. – Timtech – 2013-12-07T11:18:16.080
Umm, with those limited input values, only arbitrary precision/length integers work. Any regular floating point, etc won't work (can't store values that high). And are you talking about the infinitely many reals between those two? Also, your answer can really handle
-10^-googol(ie -10^(-10^1000), something like -0.(1000 zeros)1). If it can, can it handle-10^(-googol^(googol^(googol^googol)))? That is a real number too. And -π is not exactly representable by decimal numbers (irrational), so almost every solution here fails. – Justin – 2013-12-07T19:19:40.100@Quincunx As I said, all answers have a limit of -9E99 and 9E99. Also, pi is a real number so it must be handled. – Timtech – 2013-12-07T21:45:25.477
let us continue this discussion in chat
– Justin – 2013-12-07T23:18:58.897@Quincunx Fine with me – Timtech – 2013-12-07T23:20:20.503
2@Timtech: Can you clarify
"You may not use any built-in functions"? For example, does the GolfScript answer violate this rule when it uses the built-in split functions? Or did you just mean built-in functions that are specifically designed to calculate the absolute value? – musefan – 2013-12-09T14:08:24.4832@musefan You may not use *any* built in functions (math operators are not included, they are not functions). The GolfScript answer did violate the rule; that's why it's not accepted. – Timtech – 2013-12-09T15:50:49.803
3@tim Why don't operators count as functions? In C and friends you can override operators and use them just like normal functions. This seems to be a very vague rule – Doorknob – 2013-12-09T17:57:52.620
@Doorknob I don't use that many C-related languages. – Timtech – 2013-12-09T21:16:48.290
1Well, irrelevant - operators in those languages are functions too. (Same in many many other langs.) So why don't those count? – Doorknob – 2013-12-09T21:41:39.490
@Doorknob If math operators aren't allowed either, how would you even write valid code to do this? – Timtech – 2013-12-09T21:50:31.417
8-1. Question is vague and the definition of "built-in function" has only appeared in the comments 3 days after the question was posed. It seems like you're just looking for the shortest way to say
printf(x*(x<0?-1:1))in a number of languages. – Gareth – 2013-12-11T20:15:54.9371You say single character math operations are allowed. This means that something like python's
**should be allowed because it is exactly equivalent to^(raise to the power). Either this or other answers with powers should be disqualified. – Justin – 2013-12-14T03:22:43.693