32
7
Write the shortest program to transform the standard input into Morse code. Characters not in the table should be printed as they are.
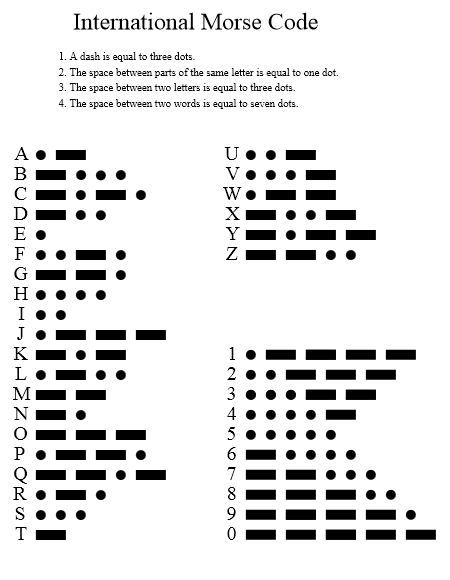
32
7
Write the shortest program to transform the standard input into Morse code. Characters not in the table should be printed as they are.

11
This answer supports only uppercase and digits. The letters are separated by newlines and words are separated by 2 newlines
{." ETIANMSURWDKGOHVF L PJBXCYZQ"?)"?/'#! 08<>"@))10%=or 2base(;{!45+}%n}%
Analysis
{ }% as usual works like a map over the array
. push a copy of the char onto the stack
" ETIAN..." this is a lookup table for the uppercase characters
? like a string.find returns the index of the char in the string
or -1 if it is not found (ie it's a digit)
) increment that index so E=>2 T=>3 I=>4 etc. notice that if the
char is not an uppercase letter or space this is now 0 (False)
"?/'#!..." this is a lookup table for the digits. it will be used in the
reverse way to the other lookup table.
@ pull that copy we made of the char to the top of the stack
))%10 convert ascii digit to a number by adding 2 and taking mod 10.
It's important to do it this way because all the uppercase
letters hit this code too, and we need to make sure they fall
in the range 0..9 or the next step will fail.
= pull the nth char from the string eg "Hello"1= gives "e"
or remember if the uppercase lookup fails we have a 0 result, so
the digit lookup will be used
2base convert to base 2 so E=>[1 0], T=>[1 1], I=>[1 0 0] etc.
(; pop the front of the list and throw it away so E=>[0], T=>[1]
{!45+}% negate each bit and add 45, this gives ascii value of . and -
n newline separates each word. this could be 32 if you wanted to
separate the words with spaces for a cost of 1 stroke
Golfscript - 85 chars
This is shorter than my SO answer due to the relaxed requirements here The input must be uppercase/digits and the punctuation characters ".,?"
{." ETIANMSURWDKGOHVF!L!PJBXCYZQ"?)"UsL?/'#! 08<>"@".,?"58,48>+?=or
2base(;{!45+}%n}%
Since the punctuation is not even required here, I may shorten the answer even more
My answer from SO
Golfscript - 107 chars
newline at the end of the input is not supported, so use something like this
echo -n Hello, Codegolfers| ../golfscript.rb morse.gs
Letters are a special case and converted to lowercase and ordered in their binary positions. Everything else is done by a translation table
' '/{{.32|"!etianmsurwdkgohvf!l!pjbxcyzq"?)"UsL?/'#! 08<>"@".,?0123456789"?=or
2base(;>{'.-'\=}%' '}%}%'/'*
The order of your code blocks here is confusing George's UserScript. Could I trouble you to rearrange? And I would like to see it explained. I get the implicit tree, but the rest is a mystery to me.
– dmckee --- ex-moderator kitten – 2011-02-13T03:03:56.033@dmckee, done. George's script noticed my count was out by one, so I fixed that too – gnibbler – 2011-02-13T03:06:55.797
Requiring upvotes to see the analysis... boo! The analysis is what makes answers worth the upvotes! – Nick Larsen – 2011-02-14T14:05:35.193
@Nick, ok I think it's as short as I can get it, so I'll get to work on that analysis – gnibbler – 2011-02-16T11:24:14.247
20
C# (213 characters)
I'm sure this wont stand long, but at least I got the technique here first!
class P{static void Main(string[] a){foreach(var t in a[0]){var c="";for(int i=" ETIANMSURWDKGOHVF L PJBXCYZQ 54 3 2 16 7 8 90".IndexOf(t);i>0;i/=2)c="-."[i--%2]+c;System.Console.Write(c+" ");}}}
And in readable format:
class P
{
static void Main(string[] a)
{
foreach(var t in a[0])
{
var c="";
for(int i=" ETIANMSURWDKGOHVF L PJBXCYZQ 54 3 2 16 7 8 90".IndexOf(t);i>0;i/=2)c="-."[i--%2]+c;
System.Console.Write(c+" ");
}
}
}
For a brief explanation, the string of characters is a heap in which the left child is a dot and the right child is a dash. To build the letter, you traverse back up and reverse the order.
1When I saw the ETIAN... in there, I assumed it worked the same as the golfscript, but you have a different way of interpreting the string. I think it is equivalent but I add 1 to the index and use the binary representation to get the dots and dashes for all the digits after the leading 1" eg F=>18=>0b10010=>..-. – gnibbler – 2011-02-13T21:23:33.583
2This is the best idea I've seen so far. – Alexandru – 2011-01-28T19:37:23.487
And then I read the linked thread and noticed this is far from original. – Nick Larsen – 2011-01-28T22:08:07.593
You don't need the space in String[] a – Cyoce – 2017-01-05T22:00:12.527
9
tr a-z A-Z | sed 's/0/--O/g;s/1/.-O/g;s/2/.J/g;s/3/..W/g;s/4/.V/g;s/5/.H/g;
s/6/-.H/g;s/7/-B/g;s/8/-Z/g;s/9/--G/g;s/X/-U/g;s/V/.U/g;s/U/.A/g;
s/Q/-K/g;s/K/-A/g;s/A/.T/g;s/J/.O/g;s/O/-M/g;s/Y/-W/g;s/W/.M/g;
s/M/-T/g;s/T/- /g;s/H/.S/g;s/B/-S/g;s/S/.I/g;s/L/.D/g;s/Z/-D/g;
s/D/-I/g;s/I/.E/g;s/C/-R/g;s/F/.R/g;s/R/.N/g;s/P/.G/g;s/G/-N/g;
s/N/-E/g;s/E/. /g'
@nabb good idea. – Eelvex – 2011-02-06T18:57:05.337
1You can drop the tr, use sed's y command instead – Hasturkun – 2011-02-13T17:52:38.857
Actually sed's y command not supports character ranges, so you have to enumerate the entire alphabet. Twice. But s/.*/\U&/ would do it, at least in GNU sed. – manatwork – 2016-01-08T14:03:39.833
1The space around a pipe could be eliminated as well ;-) – Yasir Arsanukaev – 2011-01-28T17:01:42.230
1Yes, I'm not counting those spaces, I just print them here for clarity :) – Eelvex – 2011-01-28T17:04:23.593
2You could use brace expansion to shorten it lots (/g;s/ becomes , -- plus a bit of overhead). – Nabb – 2011-02-03T12:56:49.347
6
import Data.List
i=intercalate
m=i" ".map(i" ".map(\c->words".- -... -.-. -.. . ..-. --. .... .. .--- -.- .-.. -- -. --- .--. --.- .-. ... - ..- ...- .-- -..- -.-- --.. ----- .---- ..--- ...-- ....- ..... -.... --... ---.. ----."!!(head.findIndices(==c)$['a'..'z']++['0'..'9']))).words
A more user readable form:
tbl :: [String]
tbl = words ".- -... -.-. -.. . ..-. --. .... .. .--- -.- .-.. -- -. --- .--. --.- .-. ... - ..- ...- .-- -..- -.-- --.. ----- .---- ..--- ...-- ....- ..... -.... --... ---.. ----."
lookupChar :: Char -> String
lookupChar c = tbl !! (fromJust . elemIndex c $ ['a'..'z'] ++ ['0'..'9'])
encWord :: String -> String
encWord = intercalate " " . map lookupChar
encSent :: String -> String
encSent = intercalate " " . map encWord . words
Sample run:
*Main> m "welcome humans"
".-- . .-.. -.-. --- -- . .... ..- -- .- -. ..."
There's a single whitespace between two letters, and seven whitespaces between two words.
Just checked the question referenced by @dmckee "Code Golf: Morse code" and didn't find a Haskell version. I think, shorter than 314 would be possible.
– Yasir Arsanukaev – 2011-01-28T17:33:41.507fromJust.elemIndex c can be written as head.findIndices(==c). That is one character more, but you can then get rid of import Data.Maybe, so you'll save 17 characters total. You can also save two characters by removing the space in front of the string each time you call intercalate. And another few characters by doing i=intercalate at the beginning and replacing the two calls to intercalate with i. – sepp2k – 2011-02-01T16:25:51.843
@sepp2k: Nice idea! Thanks. I also played with intercalate and have saved another 6 characters! :-) – Yasir Arsanukaev – 2011-02-01T16:54:21.730
You can also do w=words, which saves one character if I'm not mistaken. And instead of l c=... and map l, you should do map\c->... (you don't even need parens around the lambda since there's already a closing paren afterwards anyway). – sepp2k – 2011-02-01T17:02:10.783
@sepp2k: Inlining of l c=... did save me 1 character, but I couldn't put it without parens, only as map(\c->...). GHC version 6.12.3. – Yasir Arsanukaev – 2011-02-01T17:15:36.097
@Yasir: Seems I was wrong about that (didn't test it). But good that you could save a character anyway. – sepp2k – 2011-02-01T17:18:25.600
4
d=proc{|x|x>1?d[x/2]+".-"[x&1]:' '}
$><<$<.gets.bytes.map{|i|
e=i>64?"-@B4*:68,?5</.7>E20+193ACD"[(i&95)-65]:i>47?"gWOKIHX`df"[i-48]:nil
e ?d[e.ord-40]:i.chr}*''
Encodes each digit into a single char, where 1 is dash, 0 is dot, with a leading 1 as a marker bit (plus an offset to keep it printable. Uses ASCII math to use the input chars as lookup indices.
4
Module Module1
Sub Main(a$())
For Each c In a(0)
Dim i = "ETIANMSURWDKGOHVF L PJBXCYZQ 54 3 2 16 7 8 90".IndexOf(c)
If c <> " " And i >= 0 Then
Console.Write("{0} ", Morse(i))
Else
Console.Write(c)
End If
Next
End Sub
Function Morse(i) As String
Dim b = Math.Log(i) / Math.Log(2)
Return (From m In MorseSeq(If(Double.IsInfinity(b), 0, b)) Order By m.Length)(i)
End Function
Function MorseSeq(i) As IEnumerable(Of String)
Return If(i < 0, {}, From n In ".-" From m In MorseSeq(i - 1).DefaultIfEmpty
Select n & m)
End Function
End Module
That last function is evil.
edit A couple of improvements.
Function Morse(i) As String
Return (From m In MorseSeq(i) Order By m.Length)(i)
End Function
Function MorseSeq(i) As IEnumerable(Of String)
Return If(i=0,{".","-"},From n In".-"From m In MorseSeq(i>>1) Select n & m)
End Function
I decided to +1 this because I can't remember ever seeing VB.net used for golfing. – mbomb007 – 2016-01-08T20:00:16.197
4
Postscript (310) (462) (414) (319) including (46) for the table.
Combined numbers and letters with a ternary encoding. 5 ternary digits fit in a byte! This eliminates those silly difference loops, and special-casing numbers entirely.
ASCII85 cuts 1/3 of each table. And simplifying the code (finally!) gets back under 400!
errordict/undefined{pop( )dup 0 4 3 roll put print{}}put<</*{{[exch/@ cvx]cvx 1
index 1 add}forall pop}def/C{<~#:VD<!AP07"A]ga#R),'7h?+2(./s-9e6~>*}def/#{load
exec}/P{print}0{}1{(.)P}2{(---)P}/S{( )P}48<~o'u/0b'A;]L7n~>* 65 C 97 C/@{5{dup
3 mod # S 3 idiv}repeat # S S S}>>begin{(%stdin)(r)file read not{exit}if #}loop
Sample output
Luser Dr00g! . --- . . . . --- . . . . . --- . --- . . . --- . --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- . !
Ungolfed and commented. I'm very proud of this one. I feel it's elegant, making the numbers do the work. :)
%!
%Morse Code Translator (Simplified)
%if `load` signals /undefined in /#{load exec},
% pop --load--,
% print the char,
% leave dummy object for `exec` to find
errordict/undefined{pop( )dup 0 4 3 roll put print{}}put
<<
%create int->proc pairs
%from initial int and string values
/*{{[exch/@ cvx]cvx 1 index 1 add}forall pop}def
%the alpha map is applied to Upper and Lower case
/C{<~#:VD<!AP07"A]ga#R),'7h?+2(./s-9e6~>*}def
65 C 97 C
%the number map
48<~o'u/0b'A;]L7n~>*
/#{load exec} %execute a number
/P{print}
0{} % 0: nop
1{(.)P} % 1: '.' dit
2{(---)P} % 2: '---' dah
/S{( )P} % S: space
%execute a morse sequence, from the table
/@{5{dup 3 mod # S 3 idiv}repeat # S S S}
>>begin
%read and execute each char from stdin
{(%stdin)(r)file read not{exit}if #}loop
The tables (33)+(13)=(46)
Here's how the strings encode the table. Each byte represents a 5-digit ternary number. And the bytes are further encoded in ASCII85 (which postscript can automagically decode).
%The Morse Table in Ternary Encoding
% 3 ^4 ^3 ^2 ^1 ^0
% 81 27 9 3 1 Dec Hex dc ->ASCII85
% --------------- --- --- ---
% A 2 1 6+1 7 7 7 256*41+256*50+256*14+
% B 1 1 1 2 27+ 9+3+2 41 29 d85%n85/d85%n85/d85%n85/d85%n85/n
% C 1 2 1 2 27+18+3+2 50 32 2 25 53 35 27 chr(x+33)
% D 1 1 2 9+3+2 14 E # : V D <
% E 1 1 1 1
% F 1 2 1 1 27+18+3+1 49 31
% G 1 2 2 9+6+2 17 11 0 32 47 15 22
% H 1 1 1 1 27+ 9+3+1 40 28 ! A P 0 7
% I 1 1 3+1 4 4
% J 2 2 2 1 54+18+6+1 79 4F
% K 2 1 2 18+3+2 23 17 1 32 60 70 64
% L 1 1 2 1 27+ 9+6+1 43 2B " A ] g a
% M 2 2 6+2 8 8
% N 1 2 3+2 5 5
% O 2 2 2 18+6+2 26 1A 2 49 8 11 6
% P 1 2 2 1 27+18+6+1 52 34 # R ) , '
% Q 2 1 2 2 54+ 9+6+2 71 47
% R 1 2 1 9+6+1 16 10
% S 1 1 1 9+3+1 13 D 22 71 30 10 17
% T 2 2 2 2 7 h ? + 2
% U 2 1 1 18+3+1 22 16
% V 2 1 1 1 54+ 9+3+1 67 43
% W 2 2 1 18+6+1 25 19 7 13 14 82 12
% X 2 1 1 2 54+ 9+3+2 68 44 ( . / s -
% Y 2 2 1 2 54+18+3+2 77 4D 77 256*44+256*256*
% Z 1 1 2 2 27+ 9+6+2 44 2C 24 68 21 [23 36]
% 9 e 6 [ 8 E] (omit final 2)
% 0 2 2 2 2 2 162+54+18+6+2 242 F2
% 1 2 2 2 2 1 162+54+18+6+1 241 F1
% 2 2 2 2 1 1 162+54+18+3+1 238 EE 78 6 84 14 15
% 3 2 2 1 1 1 162+54+ 9+3+1 229 E5 o ' u / 0
% 4 2 1 1 1 1 162+27+ 9+3+1 202 CA
% 5 1 1 1 1 1 81+27+ 9+3+1 121 79
% 6 1 1 1 1 2 81+27+ 9+3+2 122 7A 65 6 32 26 60
% 7 1 1 1 2 2 81+27+ 9+6+2 125 7D b ' A ; ]
% 8 1 1 2 2 2 81+27+18+6+2 134 86 134 256*161+256*256*
% 9 1 2 2 2 2 81+54+18+6+2 161 A1 43 22 77 [50 40]
% L 7 n [ S I] (omit final 2)
3
Lisp (532 466 chars)
(loop(princ(let((c(read-char)))(case c(#\a".- ")(#\b"-... ")(#\c"-.-. ")(#\d"-.. ")(#\e". ")(#\f"..-. ")(#\g"--. ")(#\h".... ")(#\i".. ")(#\j".--- ")(#\k"-.- ")(#\l".-.. ")(#\m"-- ")(#\n"-. ")(#\o"--- ")(#\p".--. ")(#\q"--.- ")(#\r".-. ")(#\s"... ")(#\t"- ")(#\u"..- ")(#\v"...- ")(#\w".-- ")(#\x"-..- ")(#\y"-.-- ")(#\z"--.. ")(#\1".---- ")(#\2"..--- ")(#\3"...-- ")(#\4"....- ")(#\5"..... ")(#\6"-.... ")(#\7"--... ")(#\8"---.. ")(#\9"----. ")(#\0"----- ")(t c)))))
This encodes lower case letters, and morse code sequences are printed with a trailing space
3
In Java, 475 characters.
import java.io.*;class M{public static void main(String[]b){String s,t="-",m=t+t,o=m+t,z="",e=".",i=e+e,p=t+e,a=e+t,n=i+e,c[]={o+m,a+o,i+o,n+m,n+a,n+i,p+n,m+n,o+i,o+p,z,z,z,z,z,z,z,a,t+n,p+p,t+i,e,i+p,m+e,n+e,i,e+o,p+t,a+i,m,p,o,a+p,m+a,e+p,n,t,i+t,n+t,e+m,p+a,p+m,m+i};BufferedReader r=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));try{s=r.readLine().toUpperCase();for(int j=48;j<91;j++)s=s.replace(z+(char)j,c[j-48]+" ");System.out.println(s);}catch(Exception x){}}}
Translates a-z, A-Z and 0-9.
Edit:
Or in 447 characters, if you don't mind Java throwing an error after the translation.
import java.io.*;class M{static{String s,t="-",m=t+t,o=m+t,z="",e=".",i=e+e,p=t+e,a=e+t,n=i+e,c[]={o+m,a+o,i+o,n+m,n+a,n+i,p+n,m+n,o+i,o+p,z,z,z,z,z,z,z,a,t+n,p+p,t+i,e,i+p,m+e,n+e,i,e+o,p+t,a+i,m,p,o,a+p,m+a,e+p,n,t,i+t,n+t,e+m,p+a,p+m,m+i};BufferedReader r=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));try{s=r.readLine().toUpperCase();for(int j=48;j<91;j++)s=s.replace(z+(char)j,c[j-48]+" ");System.out.println(s);}catch(Exception x){}}}
3
Perl6 (238)
my%h="A.-B-...C-.-.D-..E.F..-.G--.H....I..J.---K-.-L.-..M--N-.O---P.--.Q--.-R.-.S...T-U..-V...-W.--X-..-Y-.--Z--..0-----1.----2..---3...--4....-5.....6-....7--...8---..9----.".split(/<wb>/)[1..72];while$*IN.getc ->$c{print %h{$c.uc}||$c}
Readable version
# Split string on word breaks to create a hash
# I get an extra token at the beginning and end for some reason
# [1..72] is a slice without the extra pieces
my %h = "A.-B-...C-.-.D-..E.F..-.G--.H....I..J.---K-.-L.-..M--N-.O---P.--.Q--.-R.-.S...T-U..-V...-W.--X-..-Y-.--Z--..0-----1.----2..---3...--4....-5.....6-....7--...8---..9----."
.split(/<wb>/)[1..72];
# For each character in STDIN, print either the looked up value, or itself
while $*IN.getc -> $c {
print %h{$c.uc} || $c;
}
"I get an extra token at the beginning and end for some reason": I don't know Perl 6, but I'd guess it's because the empty string matches before the first word boundary and after the last one. – msh210 – 2016-01-08T20:43:40.093
2
lambda a:print(*[str(ord('ӆҼzࢤpࢮyࡊoࡀѡÔÞÝࢭÓӅһѢ'[ord(c)%32])).translate(' -.'*18)for c in a])
Works on upper and lowercase.
2
char M[256] = "_^\\XP@ACGO &15)\"4+0$>-2'%/6;*(#,8.9=3", v;
main(c) {
for (;
c = getchar(), v = M[c + 208 & 255] - 32, ~c;
putchar(v-1? c : 32))
for (; v > 1; v /= 2) putchar(".-"[v & 1]);
}
(With non-significant whitespace stripped, no trailing newline)
char M[256]="_^\\XP@ACGO &15)\"4+0$>-2'%/6;*(#,8.9=3",v;main(c){for(;c=getchar(),v=M[c+208&255]-32,~c;putchar(v-1?c:32))for(;v>1;v/=2)putchar(".-"[v&1]);}
M is a lookup table where the characters' bitpatterns correspond to dots and dashes in the morse code. Characters [0-9A-Z] are decoded to morse using this table (with a space appended after the morse code), other characters are simply passed through unchanged.
Sample run:
HELLO WORLD
.... . .-.. .-.. --- .-- --- .-. .-.. -..
hello world
hello world
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789
.- -... -.-. -.. . ..-. --. .... .. .--- -.- .-.. -- -. --- .--. --.- .-. ... - ..- ...- .-- -..- -.-- --.. ----- .---- ..--- ...-- ....- ..... -.... --... ---.. ----.
That's not 162 chars... please post the golfed version. – Cyoce – 2017-01-05T22:42:46.400
@Cyoce Sorry, I didn't strip non-significant whitespace since that is a boring mechanical process and only makes it harder to read the source code, which is (used to be?) fairly standard practice on PPCG. Added a version with such whitespace stripped for you :). – FireFly – 2017-01-08T12:40:47.013
144 bytes – ceilingcat – 2019-10-10T20:45:18.517
2
s/.*/\L&/
s/[02]/&-/g
s/[89]/&./g
:
s/[b-ilnprsz5-9]/&./g
s/[ajkmoqt-y0-4]/&-/g
y/abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789/edri umsewnrttmwkai isadkgojuvhhbzoo/
t
We start by downcasing the entire line (because y can't do case-insensitive conversions); subtract 10 bytes if we are to only handle lower-case input. Then we preprocess the digits 0, 2, 8 and 9 to emit their final symbols.
The loop generates the final symbol for each input character, then translates each character for the next iteration. This is equivalent to walking up the dichotomic search table shown in the Wikipedia article; the digits that needed special treatment can be seen to have parents that are not in our ASCII alphanumerics.
The loop terminates when all characters have reached the terminating space (after 'e' or 't').
For example, the letter k is transformed in three passes:
k => k- => n-n- => n.- => t.-t.- => t-.- => -.-1
Çvy©58‹i®58-•6V%·,Õo•2B5ôsè}®64›i®64-•4…·]ÑUZ“×\ó$9™¹“ÌLÈÎ%´•3B4ôsè}"012"".- "‡})
Convert letter patterns to base-3, number patterns to base-2, use zero indexed ascii transliteration to get to periods and hyphens. Does not work on lowercase.
1
%c=("A"=>".-","B"=>"-...","C"=>"-.-.","D"=>"-..","E"=>".","F"=>"..-.","G"=>"--.","H"=>"....","I"=>"..","J"=>".---","K"=>"-.-","L"=>".-..","M"=>"--","N"=>"-.","O"=>"---","P"=>".--.","Q"=>"--.-","R"=>".-.","S"=>"...","T"=>"-","U"=>"..-","V"=>"...-","W"=>".--","X"=>"-..-","Y"=>"-.--","Z"=>"--..",1=>".----",2=>"..---",3=>"...--",4=>"..---",5=>".....",6=>"-....",7=>"--...",8=>"---..",9=>"----.",0=>"-----");while(<>){foreach(split(//)){if(exists($c{$_})){printf"%s ",$c{$_}}else{print"$_"}}}
Can be executed via command line like so.
$ perl -e '$CODE' < textfile
Edit: Thanks @tobyodavies for pointing out that my original solution had the translation backwards!
1You can get this down to 286 characters: %c=qw(A .- B -... C -.-. D -.. E . F ..-. G --. H .... I .. J .--- K -.- L .-.. M -- N -. O --- P .--. Q --.- R .-. S ... T - U ..- V ...- W .-- X -..- Y -.-- Z --.. 1 .---- 2 ..--- 3 ...-- 4 ..--- 5 ..... 6 -.... 7 --... 8 ---.. 9 ----. 0 -----);while(<>){print($c{$_}||$_)for split//} – msh210 – 2016-01-08T20:58:30.003
1
-join($args|% t*y|%{if($_-match'\w'){for($d='ihfbZJKMQY+mazzy+0;?3,>5:.H7<1/9@E42-6B8CG='[$_-48]-42;$d-1){'.-'[$d%2]
$d=$d-shr1}' '}else{$_}})
Less golfed test script:
$f = {
-join(
$args|% toCharArray|%{
if($_-match'\w'){
for($d='ihfbZJKMQY+mazzy+0;?3,>5:.H7<1/9@E42-6B8CG='[$_-48]-42;$d-1){
'.-'[$d%2]
$d=$d-shr1
}
' '
}else{
$_
}
}
)
}
@(
,("ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789",".- -... -.-. -.. . ..-. --. .... .. .--- -.- .-.. -- -. --- .--. --.- .-. ... - ..- ...- .-- -..- -.-- --.. ----- .---- ..--- ...-- ....- ..... -.... --... ---.. ----. ")
,("HELLO WORLD", ".... . .-.. .-.. --- .-- --- .-. .-.. -.. ")
,("#$%^&","#$%^&")
) | % {
$s,$expected = $_
$result = &$f $s
"$($result-eq$expected): $result"
}
Output:
True: .- -... -.-. -.. . ..-. --. .... .. .--- -.- .-.. -- -. --- .--. --.- .-. ... - ..- ...- .-- -..- -.-- --.. ----- .---- ..--- ...-- ....- ..... -.... --... ---.. ----.
True: .... . .-.. .-.. --- .-- --- .-. .-.. -..
True: #$%^&
Note: The output contains trailing spaces.
1+mazzy+ is some cheeky padding – Veskah – 2018-11-21T21:11:34.720
1
{36≥y←⍵⍳⍨⎕A,⎕D:'•-'[0∼⍨⌽(5⍴3)⊤y⊃∊(2⍴256)∘⊤¨⎕AV⍳'ܨ㈍İᄧюᜪࠄᨳ䜏ഁᙂ䴫쩸穼蚠']⋄⍵}
test:
q←{36≥y←⍵⍳⍨⎕A,⎕D:'•-'[0∼⍨⌽(5⍴3)⊤y⊃∊(2⍴256)∘⊤¨⎕AV⍳'ܨ㈍İᄧюᜪࠄᨳ䜏ഁᙂ䴫쩸穼蚠']⋄⍵}
q¨'0123456789'
----- •---- ••--- •••-- ••••- ••••• -•••• --••• ---•• ----•
q¨"HELLO WORLD"
•••• • •-•• •-•• --- •-- --- •-• •-•• -••
each letter is separated from one space, each word would be separated from 3 spaces. The table is build on alphanumeric string ⎕A,⎕D and 16bit characters 'ܨ㈍İᄧюᜪࠄᨳ䜏ഁᙂ䴫쩸穼蚠' they split in 8bit characters each converted in base 3 with reversed digits.
1
Ažh«•1Ju&àøΘn₆δβαLmSÂZΘ=+BD1
÷ΓùwÒмVšh•… .-ÅвJ#ðδJ‡
•1Ju&àøΘn₆δβαLmSÂZΘ=+BD1
÷ΓùwÒмVšh• push compressed number
… .-ÅвJ# convert to custom base " .-"
ðδJ append a space to each morse code
Ažh« ‡ transliterate
1
For both of these versions, they will put spaces between any characters. Converts 0-9 and a-z(case insensitive) are converted. A space is converted to 3.
s=>s.split("").map(e=>isNaN(d=parseInt(e.toLowerCase(),36))?e:`_OGCA@PX\\^\r\n `.charCodeAt(d).toString(2).substr(1).split("").map(e=>".-"[e]).join("")).join(" ")
Replace \n with a newline character(0x0a). It is not showing a couple of nonprintable characters because of SE. Going into edit mode shows it.
Here is the hex:
73 3d 3e 73 2e 73 70 6c 69 74 28 22 22 29 2e 6d 61 70 28 65 3d 3e 69 73 4e 61 4e 28 64 3d 70 61 72 73 65 49 6e 74 28 65 2e 74 6f 4c 6f 77 65 72 43 61 73 65 28 29 2c 33 36 29 29 3f 65 3a 60 5f 4f 47 43 41 40 50 58 5c 5c 5e 05 18 1a 0c 02 12 0e 10 04 17 5c 72 14 07 06 0f 16 1d 0a 08 03 09 11 0b 19 1b 1c 60 2e 63 68 61 72 43 6f 64 65 41 74 28 64 29 2e 74 6f 53 74 72 69 6e 67 28 32 29 2e 73 75 62 73 74 72 28 31 29 2e 73 70 6c 69 74 28 22 22 29 2e 6d 61 70 28 65 3d 3e 22 2e 2d 22 5b 65 5d 29 2e 6a 6f 69 6e 28 22 22 29 29 2e 6a 6f 69 6e 28 22 20 22 29
s=> //declare anonymous function
s.split("") //split into array of characters
.map( //for each character
e=> //declare anonymous function
isNaN( //is the character not in range 0-9a-zA-Z
d=parseInt(e.toLowerCase(),36)
//take it as base 36(digits are 0-9a-z) and assign to d
)?e: //if outside range, return as is
`_OGCA@PX\\^\r\n `
//table of the morse code as binary as code point with leading 1
.charCodeAt(d)//get the corresponding code
.toString(2) //convert to binary, 0=., 1=-, with an extra 1 bit
.substr(1) //remove the extra 1 bit
.split("") //split into each bit
.map( //for each bit
e=> //declare anonymous function
".-" //the corresponding symbol for bits
[e] //get it
)
.join("") //join the bits
)
.join(" ") //join the characters with a space between each character
s=>s.split("").map(e=>isNaN(d=parseInt(e.toLowerCase(),36))?e:[95,79,71,67,65,64,80,88,92,94,5,24,26,12,2,18,14,16,4,23,13,20,7,6,15,22,29,10,8,3,9,17,11,25,27,28][d].toString(2).substr(1).split("").map(e=>".-"[e]).join("")).join(" ")
s=> //declare anonymous function
s.split("") //split into array of characters
.map( //for each character
e=> //declare anonymous function
isNaN( //is the character not in range 0-9a-zA-Z
d=parseInt(e.toLowerCase(),36)
//take it as base 36(digits are 0-9a-z) and assign to d
)?e: //if outside range, return as is
[95,79,71,67,65,64,80,88,92,94,
5,24,26,12, 2,18,14,16, 4,23,
13,20, 7, 6,15,22,29,10, 8, 3,
9,17,11,25,27,28]
//table of the morse code as binary with leading 1
[d] //get the corresponding code
.toString(2) //convert to binary, 0=., 1=-, with an extra 1 bit
.substr(1) //remove the extra 1 bit
.split("") //split into each bit
.map( //for each bit
e=> //declare anonymous function
".-" //the corresponding symbol for bits
[e] //get it
)
.join("") //join the bits
)
.join(" ") //join the characters with a space between each character
1
<?$a=strtoupper(fgets(STDIN));$m=array(65=>".-",66=>"-...",67=>"-.-.",68=>"-..",69=>".",70=>"..-.",71=>"--.",72=>"....",73=>"..",74=>".---",75=>"-.-",76=>".-..",77=>"--",78=>"-.",79=>"---",80=>".--.",81=>"--.-",82=>".-.",83=>"...",84=>"-",85=>"..-",86=>"...-",87=>".--",88=>"-..-",89=>"-.--",90=>"--..",49=>".----",50=>"..---",51=>"...--",52=>"..---",53=>".....",54=>"-....",55=>"--...",56=>"---..",57=>"----.",48=>"-----",32=>" ");while($i++<strlen($a))echo$m[ord($a[$i])];
Its 462 characters if all input is in uppercase:
<?$a=fgets(STDIN);$m=array(65=>".-",66=>"-...",67=>"-.-.",68=>"-..",69=>".",70=>"..-.",71=>"--.",72=>"....",73=>"..",74=>".---",75=>"-.-",76=>".-..",77=>"--",78=>"-.",79=>"---",80=>".--.",81=>"--.-",82=>".-.",83=>"...",84=>"-",85=>"..-",86=>"...-",87=>".--",88=>"-..-",89=>"-.--",90=>"--..",49=>".----",50=>"..---",51=>"...--",52=>"..---",53=>".....",54=>"-....",55=>"--...",56=>"---..",57=>"----.",48=>"-----",32=>" ");while($i++<strlen($a))echo$m[ord($a[$i])];
With some minor tricks that can be reduced to: <?$a=strtoupper(fgets(STDIN));$m=array(65=>12,2111,2121,211,1,1121,221,1111,11,1222,212,1211,22,21,222,1221,2212,121,111,2,112,1112,122,2112,2122,2211)+array(48=>22222,12222,11222,11122,11222,11111,21111,22111,22211,22221)+array(32=>' ');while($a[$i++])echo strtr($m[ord($a[$i])],12,'.-'); – manatwork – 2016-01-08T14:21:42.560
0
for(;$d=ord($c=$argv[1][$i++]);)echo ctype_alnum($c)?strtr(substr(decbin(ord($d>64?".CTRH@ZF\DUGXABEVOJL?K[ISQP"[$d&31]:"]muy{|ld`^"[$c])-48),1),10,".-"):$c;
takes input from first command line argument. no pause between letters. Run with -nr.
breakdown
for(;$d=ord($c=$argv[1][$i++]);) # loop through input characters
echo # print ...
ctype_alnum($c) # if char is alphanumeric:
? strtr(
substr(
decbin(
ord($d>64 # 1. map char to char-encoded morse
?".CTRH@ZF\DUGXABEVOJL?K[ISQP"[$d&31]
:"]muy{|ld`^"[$c]
)-60 # 2. subtract 60 from ordinal value
) # 3. decbin: convert to base 2
,1) # 4. substr: skip leading `1`
,10,".-") # 5. strtr: translate binary digits to dash/dot
:$c; # not alphanumeric: no conversion
Beating JavaScript, Python2, C, Ruby and sed. I´m happy.
4th step: un-merged the mapping to handle lowercase characters without using strtoupper.
previous versions:
fail for lowercase letters; +12 bytes to fix:
Replace $argv[1] with strtoupper($argv[1]).
simple string translation, 254 bytes
<?=strtr($argv[1],["-----",".----","..---","...--","....-",".....","-....","--...","---..","----.",A=>".-","-...","-.-.","-..",".","..-.","--.","....","..",".---","-.-",".-..","--","-.","---",".--.","--.-",".-.","...","-","..-","...-",".--","-..-","-.--","--.."]);
straight forward: translates the whole string at once, character to morse code.
Save to file to execute or replace <?= with echo and run with -r.
decimal interpretation of morse codes, 184 bytes (-70)
for(;""<$c=$argv[1][$i++];)echo($m=[32,48,56,60,62,63,47,39,35,33,A=>6,23,21,11,3,29,9,31,7,24,10,27,4,5,8,25,18,13,15,2,14,30,12,22,20,19][$c])?strtr(substr(decbin($m),1),10,".-"):$c;
first golfing step: morse codes encoded to binary with an additional leading 1 to preserve leading zeroes. Loops through characters and translates them one by one. Run with -nr.
decimals encoded to character, 157 bytes (-27)
for(;""<$c=$argv[1][$i++];)echo ctype_alnum($c)?strtr(substr(decbin(ord("@"<$c?"CTRH@ZF\DUGXABEVOJL?K[ISQP"[ord($c)-65]:"]muy{|ld`^"[$c])-60),1),10,".-"):$c;
second golfing: added 60 to the decimal value and encoded to character.
merged mapping, 150 bytes (-7)
for(;""<$c=$argv[1][$i++];)echo ctype_alnum($c)?strtr(substr(decbin(ord("]muy{|ld`^8901234CTRH@ZF\DUGXABEVOJL?K[ISQP"[ord($c)-48])-60),1),10,".-"):$c;
third golfing: merged mapping for digits and letters to a single string.
0
INPUT S$WHILE""<S$B=INSTR(" ETIANMSURWDKGOHVFLPJBXCYZQ 54 3 2 16 7 8 90",S$[0])+1IF B THEN S=LOG(B,2)FOR I=0TO S-1?"._"[B-(1<<S)AND S>>I||0];:NEXT?" ";
?SHIFT(S$)*!B;
WEND
0
I created a string of alphanumerics such that their placement in the string describes their Morse code representation. Originally I was going to use binary, but 01 would be the same as 1. So I used ternary with - = 1 and . = 2. Thus is character c is at index 1121 in this string, its Morse code representation is --.-.
q,d,D=" .-"
s=" TE MN AI.OG KD.WR US-.QZ.YC XB- JP L. F VH---.09 8..7-- 6---.1-- 2..3 45".replace(D,d*3).replace(d,q*4)
lambda n:''.join(''.join([0,D,d][i]for i in [s.index(c)//3**i%3 for i in range(5)if s.index(c)//3**i!=0][::-1])+q*3 if c!=q else q*4for c in n.upper())
Test Harness
print(f("Hi")==".... .. ")
print(f("Hello")==".... . .-.. .-.. --- ")
print(f("Hello World")==".... . .-.. .-.. --- .-- --- .-. .-.. -.. ")
print(f("To be or not to be")=="- --- -... . --- .-. -. --- - - --- -... . ")
print(f("3 14 15")=="...-- .---- ....- .---- ..... ")
Update
[NOTE: There is always trailing white space but white space represents a pause, so I guest that is ok ]
1Are both capital and lowercase letters encoded? – Joey Adams – 2011-01-28T15:00:18.277
9Also, could you provide a sample input and output to clarify details like spacing between words? – Joey Adams – 2011-01-28T15:12:00.287
Well, in Morse, there's no difference between lower and upper case. There's no real symbol for space (it's just a 3/4 times silence) so I guess it should be translated as a space. – Shikiryu – 2011-01-28T15:20:24.267
@Joey: The details are up to you. – Alexandru – 2011-01-28T15:49:27.650
Similar to the Stack Overflow question Code Golf: Morse code.
– dmckee --- ex-moderator kitten – 2011-01-28T16:04:59.673Doing the reverse might be a bit more challenging. Say, with no letter separation? – Joel Cornett – 2014-01-22T16:40:06.600
How is pauses (The silence equal to one dot) encoded? – Sylwester – 2014-07-04T19:32:30.447